---
sort: 3
weight: 3
title: Kubernetes Monitoring with Managed VictoriaMetrics
menu:
docs:
parent: "managed"
weight: 3
aliases:
- /managed-victoriametrics/how-to-monitor-k8s.html
---
# Kubernetes Monitoring with Managed VictoriaMetrics
Monitoring kubernetes cluster is necessary to build SLO/SLI, to analyze performance and cost-efficiency of your workloads.
To enable enable kubernetes cluster monitoring, we will be collecting metrics about cluster performance and utilization from kubernetes components like `kube-api-server`, `kube-controller-manager`, `kube-scheduler`, `kube-state-metrics`, `etcd`, `core-dns`, `kubelet` and `kube-proxy`. We will also install some recording rules, alert rules and dashboards to provide visibility of cluster performance, as well as alerting for cluster metrics.
For node resource utilization we will be collecting metrics from `node-exporter`. We will also install dashboard and alerts for node related metrics
For workloads monitoring in kubernetes cluster we will have [VictoriaMetrics Operator](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/operator/VictoriaMetrics-Operator.html). It enables us to define scrape jobs using kubernetes CRDs [VMServiceScrape](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/operator/design.html#vmservicescrape), [VMPodScrape](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/operator/design.html#vmpodscrape). To add alerts or recording rules for workloads we can use [VMRule](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/operator/design.html#vmrule) CRD
## Overview
In this guide we will be using [victoria-metrics-k8s-stack](https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/helm-charts/tree/master/charts/victoria-metrics-k8s-stack) helm chart
This chart will install `VMOperator`, `VMAgent`, `NodeExporter`, `kube-state-metrics`, `grafana` and some service scrape configurations to start monitoring kuberentes cluster components
## Prerequisites
- Active Managed VictoriaMetrics instance. You can learn how to signup for Managed VictoriaMetrics [here](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/managed-victoriametrics/quickstart.html#how-to-register).
- Access to your kubernetes cluster
- Helm binary. You can find installation [here](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/)
## Installation steps
Install the Helm chart in a custom namespace
1. Create a unique Kubernetes namespace, for example `monitoring`
```bash
kubectl create namespace monitoring
```
2. Create kubernetes-secrets with token to access your dbaas deployment
```bash
kubectl --namespace monitoring create secret generic dbaas-write-access-token --from-literal=bearerToken=your-token
kubectl --namespace monitoring create secret generic dbaas-read-access-token --from-literal=bearerToken=your-token
```
You can find your access token on the "Access" tab of your deployment
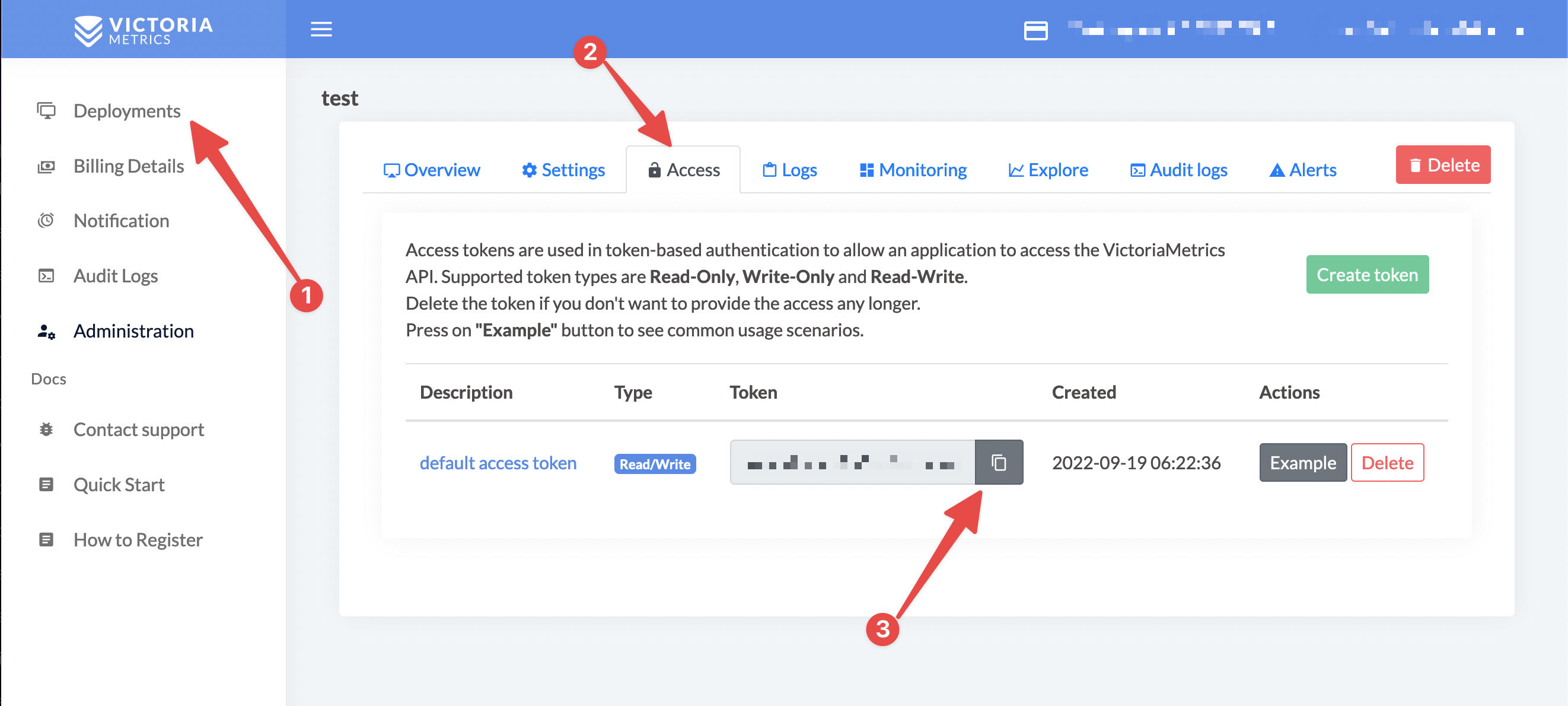 3. Set up a Helm repository using the following commands:
3. Set up a Helm repository using the following commands:
```bash
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo add vm https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
```
4. Create a YAML file of Helm values called dbaas.yaml with following content
```yaml
externalVM:
read:
url:
bearerTokenSecret:
name: dbaas-write-access-token
key: bearerToken
write:
url:
bearerTokenSecret:
name: dbaas-read-access-token
key: bearerToken
vmsingle:
enabled: false
vmcluster:
enabled: false
vmalert:
enabled: true
spec:
evaluationInterval: 15s
vmagent:
enabled: true
spec:
scrapeInterval: 30s
externalLabels:
cluster:
# dependencies
# Grafana dependency chart configuration. For possible values refer to https://github.com/grafana/helm-charts/tree/main/charts/grafana#configuration
grafana:
enabled: true
```
5. Install VictoriaMetrics-k8s-stack helm chart
```bash
helm --namespace monitoring install vm vm/victoria-metrics-k8s-stack -f dbaas.yaml -n monitoring
```
## Connect grafana
Connect to grafana and create your datasource
> If you are using external grafana, you can skip steps 1-3 and you will need to import dashboards that can be found here manually
1. Get grafana password
```bash
kubectl --namespace monitoring get secret vm-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 -d
```
2. Connect to grafana
```bash
kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward service/vm-grafana 3000:80
```
3. Open grafana in your browser [http://localhost:3000/datasources](http://localhost:3000/datasources)
Use admin as username and password from previous step
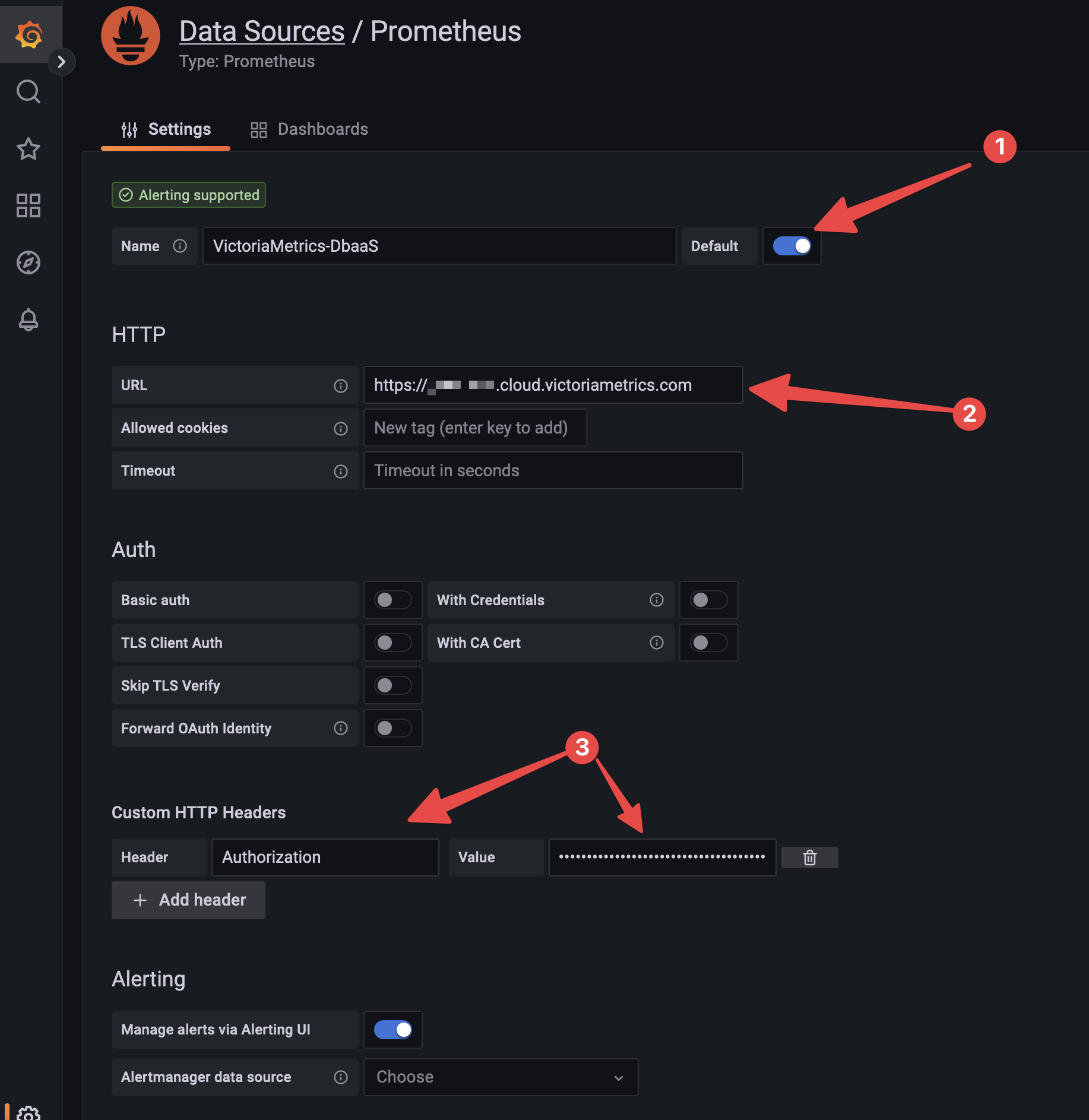
4. Click on add datasource
Choose VictoriaMetrics or Prometheus as datasource type. Make sure you made this datasource as default for dashboards to work.
> You can find token and URL in your deployment, on Access tab
 ## Test it
- You should be able to see data that was sent to your dbaas using VMAgent dashboard [http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/](http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/)
- You also will be able to see bunch of kuberentes dashboards in your grafana
## Test it
- You should be able to see data that was sent to your dbaas using VMAgent dashboard [http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/](http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/)
- You also will be able to see bunch of kuberentes dashboards in your grafana
 3. Set up a Helm repository using the following commands:
3. Set up a Helm repository using the following commands:
 ## Test it
- You should be able to see data that was sent to your dbaas using VMAgent dashboard [http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/](http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/)
- You also will be able to see bunch of kuberentes dashboards in your grafana
## Test it
- You should be able to see data that was sent to your dbaas using VMAgent dashboard [http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/](http://localhost:3000/d/G7Z9GzMGz/victoriametrics-vmagent/)
- You also will be able to see bunch of kuberentes dashboards in your grafana