# Kubernetes monitoring via VictoriaMetrics Single
**This guide covers:**
* The setup of a [VictoriaMetrics Single](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html) in [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/) via Helm charts
* How to scrape metrics from k8s components using service discovery
* How to visualize stored data
* How to store metrics in [VictoriaMetrics](https://victoriametrics.com) tsdb
**Precondition**
We will use:
* [Kubernetes cluster 1.19.9-gke.1900](https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine)
> We use GKE cluster from [GCP](https://cloud.google.com/) but this guide is also applied on any Kubernetes cluster. For example [Amazon EKS](https://aws.amazon.com/ru/eks/).
* [Helm 3 ](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install)
* [kubectl 1.21](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl)
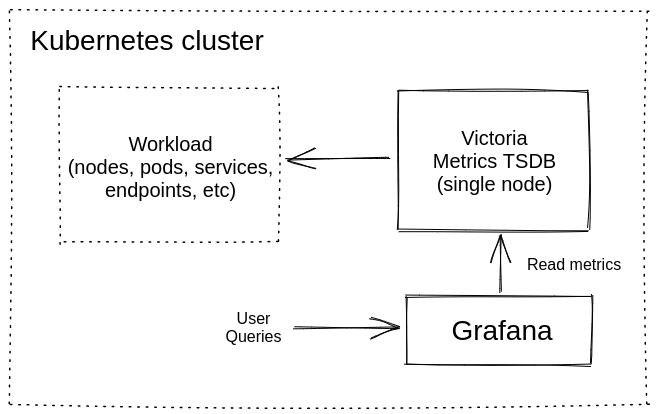
## 1. VictoriaMetrics Helm repository
> For this guide we will use Helm 3 but if you already use Helm 2 please see this [https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/helm-charts#for-helm-v2](https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/helm-charts#for-helm-v2)
You need to add the VictoriaMetrics Helm repository to install VictoriaMetrics components. We’re going to use [VictoriaMetrics Single](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html). You can do this by running the following command:
```bash
helm repo add vm https://victoriametrics.github.io/helm-charts/
```
Update Helm repositories:
```bash
helm repo update
```
To verify that everything is set up correctly you may run this command:
```bash
helm search repo vm/
```
The expected output is:
```bash
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
vm/victoria-metrics-agent 0.7.20 v1.62.0 Victoria Metrics Agent - collects metrics from ...
vm/victoria-metrics-alert 0.3.34 v1.62.0 Victoria Metrics Alert - executes a list of giv...
vm/victoria-metrics-auth 0.2.23 1.62.0 Victoria Metrics Auth - is a simple auth proxy ...
vm/victoria-metrics-cluster 0.8.32 1.62.0 Victoria Metrics Cluster version - high-perform...
vm/victoria-metrics-k8s-stack 0.2.9 1.16.0 Kubernetes monitoring on VictoriaMetrics stack....
vm/victoria-metrics-operator 0.1.17 0.16.0 Victoria Metrics Operator
vm/victoria-metrics-single 0.7.5 1.62.0 Victoria Metrics Single version - high-performa...
```
## 2. Install [VictoriaMetrics Single](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html) from Helm Chart
Run this command in your terminal:
.html
```bash
helm install vmsingle vm/victoria-metrics-single -f https://docs.victoriametrics.com/guides/guide-vmsingle-values.yaml
```
Here is full file content `guide-vmsingle-values.yaml`
```yaml
server:
scrape:
enabled: true
configMap: ""
config:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: victoriametrics
static_configs:
- targets: [ "localhost:8428" ]
- job_name: "kubernetes-apiservers"
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
relabel_configs:
- source_labels:
[
__meta_kubernetes_namespace,
__meta_kubernetes_service_name,
__meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name,
]
action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
- job_name: "kubernetes-nodes"
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [ __meta_kubernetes_node_name ]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics
- job_name: "kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor"
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: true
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
- source_labels: [ __meta_kubernetes_node_name ]
regex: (.+)
target_label: __metrics_path__
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
metric_relabel_configs:
- action: replace
source_labels: [pod]
regex: '(.+)'
target_label: pod_name
replacement: '${1}'
- action: replace
source_labels: [container]
regex: '(.+)'
target_label: container_name
replacement: '${1}'
- action: replace
target_label: name
replacement: k8s_stub
- action: replace
source_labels: [id]
regex: '^/system\.slice/(.+)\.service$'
target_label: systemd_service_name
replacement: '${1}'
```
* By running `helm install vmsingle vm/victoria-metrics-single` we install [VictoriaMetrics Single](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html) to default [namespace](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/namespaces/) inside your cluster
* By adding `scrape: enable: true` we add and enable autodiscovery scraping from kubernetes cluster to [VictoriaMetrics Single](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/Single-server-VictoriaMetrics.html)
* On line 166 from [https://docs.victoriametrics.com/guides/guide-vmsingle-values.yaml](https://docs.victoriametrics.com/guides/guide-vmsingle-values.yaml) we added `metric_relabel_configs` section that will help us to show Kubernetes metrics on Grafana dashboard.
As a result of the command you will see the following output:
```bash
NAME: victoria-metrics
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jun 25 12:06:13 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
The VictoriaMetrics write api can be accessed via port 8428 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local
Metrics Ingestion:
Get the Victoria Metrics service URL by running these commands in the same shell:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app=server" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 8428
Write url inside the kubernetes cluster:
http://vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local:8428/api/v1/write
Metrics Scrape:
Pull-based scrapes are enabled
Scrape config can be displayed by running this command::
kubectl get cm vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server-scrapeconfig -n default
The target’s information is accessible via api:
Inside cluster:
http://vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local:8428/targets
Outside cluster:
You need to port-forward service (see instructions above) and call
http:///targets
Read Data:
The following url can be used as the datasource url in Grafana::
http://vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server.default.svc.cluster.local:8428
```
For us it’s important to remember the url for the datasource (copy lines from output).
Verify that VictoriaMetrics pod is up and running by executing the following command:
```bash
kubectl get pods
```
The expected output is:
```bash
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
vmsingle-victoria-metrics-single-server-0 1/1 Running 0 68s
```
## 3. Install and connect Grafana to VictoriaMetrics with Helm
Add the Grafana Helm repository.
```bash
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
```
By installing the Chart with the release name `my-grafana`, you add the VictoriaMetrics datasource with official dashboard and kubernetes dashboard:
```yaml
cat <
By running this command we:
* Install Grafana from Helm repository.
* Provision VictoriaMetrics datasource with the url from the output above which we copied before.
* Add this [https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/10229](https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/10229) dashboard for VictoriaMetrics.
* Add this [https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/14205](https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/14205) dashboard to see Kubernetes cluster metrics.
Check the output log in your terminal.
To see the password for Grafana `admin` user use the following command:
```bash
kubectl get secret --namespace default my-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode ; echo
```
Expose Grafana service on `127.0.0.1:3000`:
```bash
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=grafana,app.kubernetes.io/instance=my-grafana" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $POD_NAME 3000
```
Now Grafana should be accessible on the [http://127.0.0.1:3000](http://127.0.0.1:3000) address.
## 4. Check the obtained result in your browser
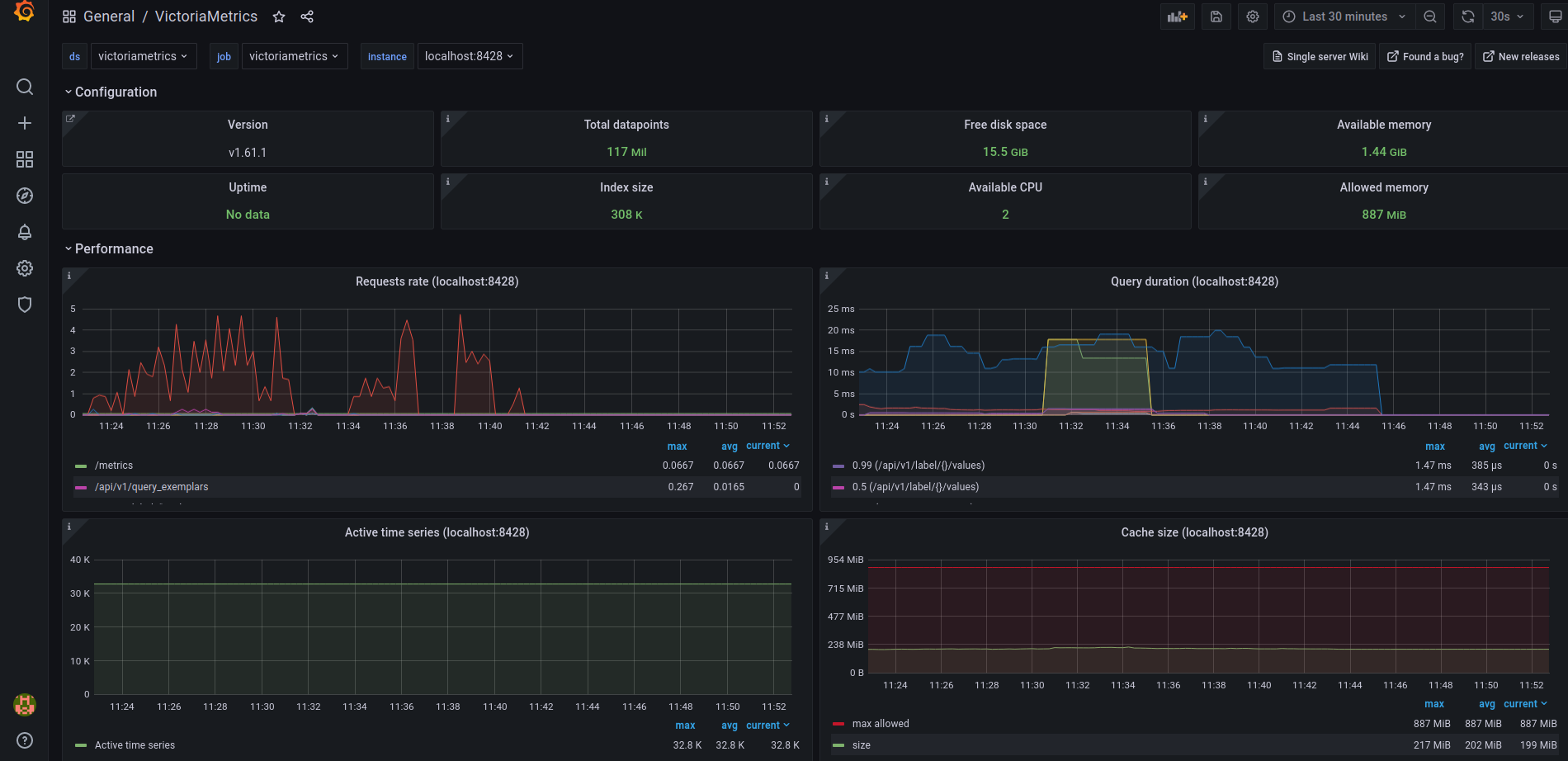
To check that VictoriaMetrics has collects metrics from the k8s cluster open in browser [http://127.0.0.1:3000/dashboards](http://127.0.0.1:3000/dashboards) and choose `Kubernetes Cluster Monitoring (via Prometheus)` dashboard. Use `admin` for login and `password` that you previously obtained from kubectl.

You will see something like this:

VictoriaMetrics dashboard also available to use:
## 5. Final thoughts
* We have set up TimeSeries Database for your k8s cluster.
* Collected metrics from all running pods,nodes, … and store them in VictoriaMetrics database.
* Visualize resources used in Kubernetes cluster by Grafana dashboards.




