98 KiB
vmagent
vmagent is a tiny but mighty agent which helps you collect metrics from various sources
and store them in VictoriaMetrics
or any other Prometheus-compatible storage systems with Prometheus remote_write protocol support.
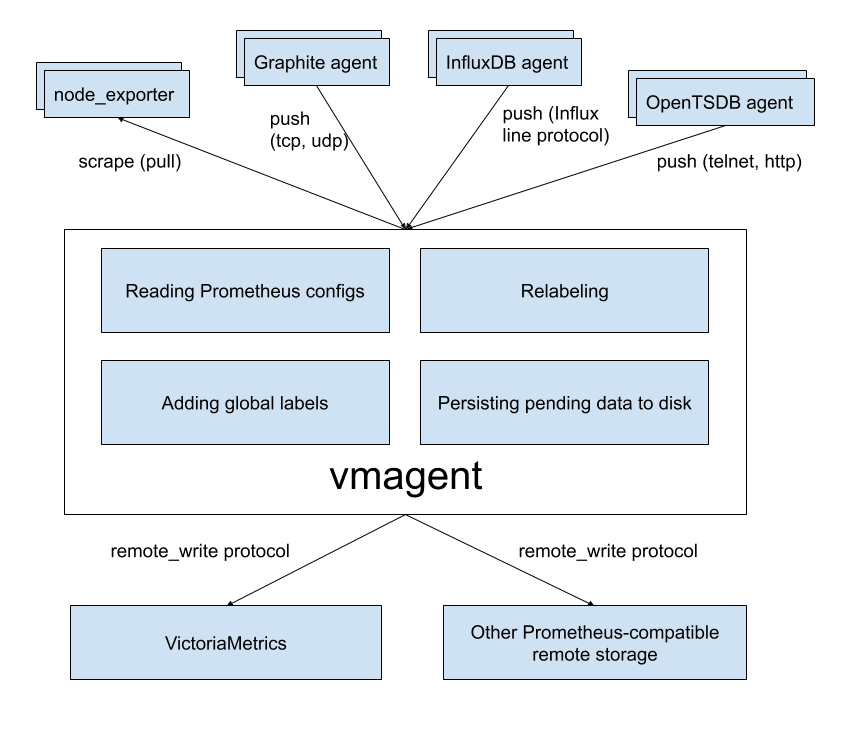
Motivation
While VictoriaMetrics provides an efficient solution to store and observe metrics, our users needed something fast
and RAM friendly to scrape metrics from Prometheus-compatible exporters into VictoriaMetrics.
Also, we found that our user's infrastructure are like snowflakes in that no two are alike. Therefore we decided to add more flexibility
to vmagent such as the ability to accept metrics via popular push protocols
additionally to discovering Prometheus-compatible targets and scraping metrics from them.
Features
- Can be used as a drop-in replacement for Prometheus for scraping targets such as node_exporter. See Quick Start for details.
- Can read data from Kafka. See these docs.
- Can write data to Kafka. See these docs.
- Can add, remove and modify labels (aka tags) via Prometheus relabeling. Can filter data before sending it to remote storage. See these docs for details.
- Accepts data via all the ingestion protocols supported by VictoriaMetrics - see these docs.
- Can replicate collected metrics simultaneously to multiple remote storage systems.
- Works smoothly in environments with unstable connections to remote storage. If the remote storage is unavailable, the collected metrics
are buffered at
-remoteWrite.tmpDataPath. The buffered metrics are sent to remote storage as soon as the connection to the remote storage is repaired. The maximum disk usage for the buffer can be limited with-remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURL. - Uses lower amounts of RAM, CPU, disk IO and network bandwidth compared with Prometheus.
- Scrape targets can be spread among multiple
vmagentinstances when big number of targets must be scraped. See these docs. - Can efficiently scrape targets that expose millions of time series such as /federate endpoint in Prometheus. See these docs.
- Can deal with high cardinality and high churn rate issues by limiting the number of unique time series at scrape time and before sending them to remote storage systems. See these docs.
- Can load scrape configs from multiple files. See these docs.
Quick Start
Please download vmutils-* archive from releases page (vmagent is also available in docker images), unpack it and pass the following flags to the vmagent binary in order to start scraping Prometheus-compatible targets:
-promscrape.configwith the path to Prometheus config file (usually located at/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml). The path can point either to local file or to http url.vmagentdoesn't support some sections of Prometheus config file, so you may need either to delete these sections or to runvmagentwith-promscrape.config.strictParse=falsecommand-line flag, sovmagentignores unsupported sections. See the list of unsupported sections.-remoteWrite.urlwith the remote storage endpoint such as VictoriaMetrics, the-remoteWrite.urlargument can be specified multiple times to replicate data concurrently to an arbitrary number of remote storage systems.
Example command line:
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.config=/path/to/prometheus.yml -remoteWrite.url=https://victoria-metrics-host:8428/api/v1/write
See how to scrape Prometheus-compatible targets for more details.
If you don't need to scrape Prometheus-compatible targets, then the -promscrape.config option isn't needed. For example, the following command is sufficient for accepting data via supported "push"-based protocols and sending it to the provided -remoteWrite.url:
/path/to/vmagent -remoteWrite.url=https://victoria-metrics-host:8428/api/v1/write
See troubleshooting docs if you encounter common issues with vmagent.
Pass -help to vmagent in order to see the full list of supported command-line flags with their descriptions.
How to push data to vmagent
vmagent supports the same set of push-based data ingestion protocols as VictoriaMetrics does additionally to pull-based Prometheus-compatible targets' scraping:
- DataDog "submit metrics" API. See these docs.
- InfluxDB line protocol via
http://<vmagent>:8429/write. See these docs. - Graphite plaintext protocol if
-graphiteListenAddrcommand-line flag is set. See these docs. - OpenTSDB telnet and http protocols if
-opentsdbListenAddrcommand-line flag is set. See these docs. - Prometheus remote write protocol via
http://<vmagent>:8429/api/v1/write. - JSON lines import protocol via
http://<vmagent>:8429/api/v1/import. See these docs. - Native data import protocol via
http://<vmagent>:8429/api/v1/import/native. See these docs. - Prometheus exposition format via
http://<vmagent>:8429/api/v1/import/prometheus. See these docs for details. - Arbitrary CSV data via
http://<vmagent>:8429/api/v1/import/csv. See these docs.
Configuration update
vmagent should be restarted in order to update config options set via command-line args.
vmagent supports multiple approaches for reloading configs from updated config files such as -promscrape.config, -remoteWrite.relabelConfig and -remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig:
-
Sending
SUGHUPsignal tovmagentprocess:kill -SIGHUP `pidof vmagent` -
Sending HTTP request to
http://vmagent:8429/-/reloadendpoint.
There is also -promscrape.configCheckInterval command-line option, which can be used for automatic reloading configs from updated -promscrape.config file.
Use cases
IoT and Edge monitoring
vmagent can run and collect metrics in IoT environments and industrial networks with unreliable or scheduled connections to their remote storage.
It buffers the collected data in local files until the connection to remote storage becomes available and then sends the buffered
data to the remote storage. It re-tries sending the data to remote storage until errors are resolved.
The maximum on-disk size for the buffered metrics can be limited with -remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURL.
vmagent works on various architectures from the IoT world - 32-bit arm, 64-bit arm, ppc64, 386, amd64.
See the corresponding Makefile rules for details.
Drop-in replacement for Prometheus
If you use Prometheus only for scraping metrics from various targets and forwarding these metrics to remote storage
then vmagent can replace Prometheus. Typically, vmagent requires lower amounts of RAM, CPU and network bandwidth compared with Prometheus.
See these docs for details.
Flexible metrics relay
vmagent can accept metrics in various popular data ingestion protocols, apply relabeling to the accepted metrics (for example, change metric names/labels or drop unneeded metrics) and then forward the relabeled metrics to other remote storage systems, which support Prometheus remote_write protocol (including other vmagent instances).
Replication and high availability
vmagent replicates the collected metrics among multiple remote storage instances configured via -remoteWrite.url args.
If a single remote storage instance temporarily is out of service, then the collected data remains available in another remote storage instance.
vmagent buffers the collected data in files at -remoteWrite.tmpDataPath until the remote storage becomes available again and then it sends the buffered data to the remote storage in order to prevent data gaps.
Relabeling and filtering
vmagent can add, remove or update labels on the collected data before sending it to the remote storage. Additionally,
it can remove unwanted samples via Prometheus-like relabeling before sending the collected data to remote storage.
Please see these docs for details.
Splitting data streams among multiple systems
vmagent supports splitting the collected data between multiple destinations with the help of -remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig,
which is applied independently for each configured -remoteWrite.url destination. For example, it is possible to replicate or split
data among long-term remote storage, short-term remote storage and a real-time analytical system built on top of Kafka.
Note that each destination can receive it's own subset of the collected data due to per-destination relabeling via -remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig.
Prometheus remote_write proxy
vmagent can be used as a proxy for Prometheus data sent via Prometheus remote_write protocol. It can accept data via the remote_write API
at the/api/v1/write endpoint. Then apply relabeling and filtering and proxy it to another remote_write system .
The vmagent can be configured to encrypt the incoming remote_write requests with -tls* command-line flags.
Also, Basic Auth can be enabled for the incoming remote_write requests with -httpAuth.* command-line flags.
remote_write for clustered version
While vmagent can accept data in several supported protocols (OpenTSDB, Influx, Prometheus, Graphite) and scrape data from various targets, writes are always performed in Promethes remote_write protocol. Therefore for the clustered version, -remoteWrite.url the command-line flag should be configured as <schema>://<vminsert-host>:8480/insert/<accountID>/prometheus/api/v1/write according to these docs. There is also support for multitenant writes. See these docs.
Multitenancy
By default vmagent collects the data without tenant identifiers and routes it to the configured -remoteWrite.url.
Multitenancy support is enabled when -remoteWrite.multitenantURL command-line flag is set. In this case vmagent accepts multitenant data at http://vmagent:8429/insert/<accountID>/... in the same way as cluster version of VictoriaMetrics does according to these docs and routes it to <-remoteWrite.multitenantURL>/insert/<accountID>/prometheus/api/v1/write. If multiple -remoteWrite.multitenantURL command-line options are set, then vmagent replicates the collected data across all the configured urls. This allows using a single vmagent instance in front of VictoriaMetrics clusters for processing the data from all the tenants.
If -remoteWrite.multitenantURL command-line flag is set and vmagent is configured to scrape Prometheus-compatible targets (e.g. if -promscrape.config command-line flag is set)
then vmagent reads tenantID from __tenant_id__ label for the discovered targets and routes all the metrics from this target to the given __tenant_id__, e.g. to the url <-remoteWrite.multitnenatURL>/insert/<__tenant_id__>/prometheus/api/v1/write.
For example, the following relabeling rule instructs sending metrics to tenantID defined in the prometheus.io/tenant annotation of Kubernetes pod deployment:
scrape_configs:
- kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_tenant]
target_label: __tenant_id__
If the target has no associated __tenant_id__ label, then its' metrics are routed to zero tenantID, e.g. to <-remoteWrite.multitenantURL>/insert/0/prometheus/api/v1/write.
How to collect metrics in Prometheus format
Specify the path to prometheus.yml file via -promscrape.config command-line flag. vmagent takes into account the following
sections from Prometheus config file:
globalscrape_configs
All other sections are ignored, including the remote_write section.
Use -remoteWrite.* command-line flag instead for configuring remote write settings. See the list of unsupported config sections.
The file pointed by -promscrape.config may contain %{ENV_VAR} placeholders which are substituted by the corresponding ENV_VAR environment variable values.
See the list of supported service discovery types for Prometheus scrape targets.
scrape_config enhancements
vmagent supports the following additional options in scrape_configs section:
headers- a list of HTTP headers to send to scrape target with each scrape request. This can be used when the scrape target needs custom authorization and authentication. For example:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: custom_headers
headers:
- "TenantID: abc"
- "My-Auth: TopSecret"
disable_compression: truefor disabling response compression on a per-job basis. By defaultvmagentrequests compressed responses from scrape targets for saving network bandwidth.disable_keepalive: truefor disabling HTTP keep-alive connections on a per-job basis. By defaultvmagentuses keep-alive connections to scrape targets for reducing overhead on connection re-establishing.series_limit: Nfor limiting the number of unique time series a single scrape target can expose. See these docs.stream_parse: truefor scraping targets in a streaming manner. This may be useful when targets export big number of metrics. See these docs.scrape_align_interval: durationfor aligning scrapes to the given interval instead of using random offset in the range[0 ... scrape_interval]for scraping each target. The random offset helps spreading scrapes evenly in time.scrape_offset: durationfor specifying the exact offset for scraping instead of using random offset in the range[0 ... scrape_interval].relabel_debug: truefor enabling debug logging during relabeling of the discovered targets. See these docs.metric_relabel_debug: truefor enabling debug logging during relabeling of the scraped metrics. See these docs.
Loading scrape configs from multiple files
vmagent supports loading scrape configs from multiple files specified in the scrape_config_files section of -promscrape.config file. For example, the following -promscrape.config instructs vmagent loading scrape configs from all the *.yml files under configs directory, from single_scrape_config.yml local file and from https://config-server/scrape_config.yml url:
scrape_config_files:
- configs/*.yml
- single_scrape_config.yml
- https://config-server/scrape_config.yml
Every referred file can contain arbitrary number of supported scrape configs. There is no need in specifying top-level scrape_configs section in these files. For example:
- job_name: foo
static_configs:
- targets: ["vmagent:8429"]
- job_name: bar
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
vmagent is able to dynamically reload these files - see these docs.
Unsupported Prometheus config sections
vmagent doesn't support the following sections in Prometheus config file passed to -promscrape.config command-line flag:
- remote_write. This section is substituted with various
-remoteWrite*command-line flags. See the full list of flags. Theremote_writesection isn't supported in order to reduce possible confusion whenvmagentis used for accepting incoming metrics via supported push protocols. In this case the-promscrape.configfile isn't needed. remote_read. This section isn't supported at all, sincevmagentdoesn't provide Prometheus querying API. It is expected that the querying API is provided by the remote storage specified via-remoteWrite.urlsuch as VictoriaMetrics. See Prometheus querying API docs for VictoriaMetrics.rule_filesandalerting. These sections are supported by vmalert.
The list of supported service discovery types is available here.
Additionally vmagent doesn't support refresh_interval option at service discovery sections. This option is substituted with -promscrape.*CheckInterval command-line options, which are specific per each service discovery type. See the full list of command-line flags for vmagent.
Adding labels to metrics
Extra labels can be added to metrics collected by vmagent via the following mechanisms:
- The
global -> external_labelssection in-promscrape.configfile. These labels are added only to metrics scraped from targets configured in the-promscrape.configfile. They aren't added to metrics collected via other data ingestion protocols. - The
-remoteWrite.labelcommand-line flag. These labels are added to all the collected metrics before sending them to-remoteWrite.url. For example, the following command startsvmagent, which adds{datacenter="foobar"}label to all the metrics pushed to all the configured remote storage systems (all the-remoteWrite.urlflag values):
/path/to/vmagent -remoteWrite.label=datacenter=foobar ...
- Via relabeling. See these docs.
Automatically generated metrics
vmagent automatically generates the following metrics per each scrape of every Prometheus-compatible target:
-
up- this metric exposes1value on successful scrape and0value on unsuccessful scrape. This allows monitoring failing scrapes with the following MetricsQL query:up == 0 -
scrape_duration_seconds- this metric exposes scrape duration. This allows monitoring slow scrapes. For example, the following MetricsQL query returns scrapes, which take more than 1.5 seconds to complete:scrape_duration_seconds > 1.5 -
scrape_timeout_seconds- this metric exposes the configured timeout for the current scrape target (akascrape_timeout). This allows detecting targets with scrape durations close to the configured scrape timeout. For example, the following MetricsQL query returns targets (identified byinstancelabel), which take more than 80% of the configuredscrape_timeoutduring scrapes:scrape_duration_seconds / scrape_timeout_seconds > 0.8 -
scrape_samples_scraped- this metric exposes the number of samples (aka metrics) parsed per each scrape. This allows detecting targets, which expose too many metrics. For example, the following MetricsQL query returns targets, which expose more than 10000 metrics:scrape_samples_scraped > 10000 -
scrape_samples_limit- this metric exposes the configured limit on the number of metrics the given target can expose. The limit can be set viasample_limitoption at scrape_configs. This allows detecting targets, which expose too many metrics compared to the configuredsample_limit. For example, the following query returns targets (identified byinstancelabel), which expose more than 80% metrics compared to the configedsample_limit:scrape_samples_scraped / scrape_samples_limit > 0.8 -
scrape_samples_post_metric_relabeling- this metric exposes the number of samples (aka metrics) left after applying metric-level relabeling frommetric_relabel_configssection (see relabeling docs for more details). This allows detecting targets with too many metrics after the relabeling. For example, the following MetricsQL query returns targets with more than 10000 metrics after the relabeling:scrape_samples_post_metric_relabeling > 10000 -
scrape_series_added- this metric exposes an approximate number of new series the given target generates during the current scrape. This metric allows detecting targets (identified byinstancelabel), which lead to high churn rate. For example, the following MetricsQL query returns targets, which generate more than 1000 new series during the last hour:sum_over_time(scrape_series_added[1h]) > 1000vmagentsetsscrape_series_addedto zero when it runs with-promscrape.noStaleMarkerscommand-line option (e.g. when staleness markers are disabled).
Relabeling
VictoriaMetrics components (including vmagent) support Prometheus-compatible relabeling with additional enhancements at various stages of data processing. The relabeling can be defined in the following places processed by vmagent:
- At the
scrape_config -> relabel_configssection in-promscrape.configfile. This relabeling is used for modifying labels in discovered targets and for dropping unneded targets. This relabeling can be debugged by passingrelabel_debug: trueoption to the correspondingscrape_configsection. In this casevmagentlogs target labels before and after the relabeling and then drops the logged target. - At the
scrape_config -> metric_relabel_configssection in-promscrape.configfile. This relabeling is used for modifying labels in scraped metrics and for dropping unneeded metrics. This relabeling can be debugged by passingmetric_relabel_debug: trueoption to the correspondingscrape_configsection. In this casevmagentlogs metrics before and after the relabeling and then drops the logged metrics. - At the
-remoteWrite.relabelConfigfile. This relabeling is used for modifying labels for all the collected metrics (inluding metrics obtained via push-based protocols) and for dropping unneeded metrics before sending them to all the configured-remoteWrite.urladdresses. This relabeling can be debugged by passing-remoteWrite.relabelDebugcommand-line option tovmagent. In this casevmagentlogs metrics before and after the relabeling and then drops all the logged metrics instead of sending them to remote storage. - At the
-remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfigfiles. This relabeling is used for modifying labels for metrics and for dropping unneeded metrics before sending them to a particular-remoteWrite.url. This relabeling can be debugged by passing-remoteWrite.urlRelabelDebugcommand-line options tovmagent. In this casevmagentlogs metrics before and after the relabeling and then drops all the logged metrics instead of sending them to the corresponding-remoteWrite.url.
All the files with relabeling configs can contain special placeholders in the form %{ENV_VAR}, which are replaced by the corresponding environment variable values.
The following articles contain useful information about Prometheus relabeling:
- How to use Relabeling in Prometheus and VictoriaMetrics
- Life of a label
- Discarding targets and timeseries with relabeling
- Dropping labels at scrape time
- Extracting labels from legacy metric names
- relabel_configs vs metric_relabel_configs
This relabeler playground can help debugging issues related to relabeling.
Relabeling enhancements
VictoriaMetrics provides the following additional relabeling actions on top of standard actions from the Prometheus relabeling:
-
replace_allreplaces all of the occurrences ofregexin the values ofsource_labelswith thereplacementand stores the results in thetarget_label. For example, the following relabeling config replaces all the occurrences of-char in metric names with_char (e.g.foo-bar-bazmetric name is transformed intofoo_bar_baz):- action: replace_all source_labels: ["__name__"] target_label: "__name__" regex: "-" replacement: "_" -
labelmap_allreplaces all of the occurrences ofregexin all the label names with thereplacement. For example, the following relabeling config replaces all the occurrences of-char in all the label names with_char (e.g.foo-bar-bazlabel name is transformed intofoo_bar_baz):- action: labelmap_all regex: "-" replacement: "_" -
keep_if_equal: keeps the entry if all the label values fromsource_labelsare equal, while dropping all the other entries. For example, the following relabeling config keeps targets if they contain equal values forinstanceandhostlabels, while dropping all the other targets:- action: keep_if_equal source_labels: ["instance", "host"] -
drop_if_equal: drops the entry if all the label values fromsource_labelsare equal, while keeping all the other entries. For example, the following relabeling config drops targets if they contain equal values forinstanceandhostlabels, while keeping all the other targets:- action: drop_if_equal source_labels: ["instance", "host"] -
keep_metrics: keeps all the metrics with names matching the givenregex, while dropping all the other metrics. For example, the following relabeling config keeps metrics withfoandbarnames, while dropping all the other metrics:- action: keep_metrics regex: "foo|bar" -
drop_metrics: drops all the metrics with names matching the givenregex, while keeping all the other metrics. For example, the following relabeling config drops metrics withfooandbarnames, while leaving all the other metrics:- action: drop_metrics regex: "foo|bar" -
graphite: applies Graphite-style relabeling to metric name. See these docs for details.
The regex value can be split into multiple lines for improved readability and maintainability. These lines are automatically joined with | char when parsed. For example, the following configs are equivalent:
- action: keep_metrics
regex: "metric_a|metric_b|foo_.+"
- action: keep_metrics
regex:
- "metric_a"
- "metric_b"
- "foo_.+"
VictoriaMetrics components support an optional if filter in relabeling configs, which can be used for conditional relabeling. The if filter may contain arbitrary time series selector. For example, the following relabeling rule drops metrics, which don't match foo{bar="baz"} series selector, while leaving the rest of metrics:
- action: keep
if: 'foo{bar="baz"}'
This is equivalent to less clear Prometheus-compatible relabeling rule:
- action: keep
source_labels: [__name__, bar]
regex: 'foo;baz'
Graphite relabeling
VictoriaMetrics components support action: graphite relabeling rules, which allow extracting various parts from Graphite-style metrics
into the configured labels with the syntax similar to Glob matching in statsd_exporter.
Note that the name field must be substituted with explicit __name__ option under labels section.
If __name__ option is missing under labels section, then the original Graphite-style metric name is left unchanged.
For example, the following relabeling rule generates requests_total{job="app42",instance="host124:8080"} metric
from "app42.host123.requests.total" Graphite-style metric:
- action: graphite
match: "*.*.*.total"
labels:
__name__: "${3}_total"
job: "$1"
instance: "${2}:8080"
Important notes about action: graphite relabeling rules:
- The relabeling rule is applied only to metrics, which match the given
matchexpression. Other metrics remain unchanged. - The
*matches the maximum possible number of chars until the next dot or until the next part of thematchexpression whichever comes first. It may match zero chars if the next char is.. For example,match: "app*foo.bar"matchesapp42foo.barand42becomes available to use atlabelssection via$1capture group. - The
$0capture group matches the original metric name. - The relabeling rules are executed in order defined in the original config.
The action: graphite relabeling rules are easier to write and maintain than action: replace for labels extraction from Graphite-style metric names.
Additionally, the action: graphite relabeling rules usually work much faster than the equivalent action: replace rules.
Prometheus staleness markers
vmagent sends Prometheus staleness markers to -remoteWrite.url in the following cases:
- If they are passed to
vmagentvia Prometheus remote_write protocol. - If the metric disappears from the list of scraped metrics, then stale marker is sent to this particular metric.
- If the scrape target becomes temporarily unavailable, then stale markers are sent for all the metrics scraped from this target.
- If the scrape target is removed from the list of targets, then stale markers are sent for all the metrics scraped from this target.
Prometheus staleness markers' tracking needs additional memory, since it must store the previous response body per each scrape target in order to compare it to the current response body. The memory usage may be reduced by passing -promscrape.noStaleMarkers command-line flag to vmagent. This disables staleness tracking. This also disables tracking the number of new time series per each scrape with the auto-generated scrape_series_added metric. See these docs for details.
Stream parsing mode
By default vmagent reads the full response body from scrape target into memory, then parses it, applies relabeling and then pushes the resulting metrics to the configured -remoteWrite.url. This mode works good for the majority of cases when the scrape target exposes small number of metrics (e.g. less than 10 thousand). But this mode may take big amounts of memory when the scrape target exposes big number of metrics. In this case it is recommended enabling stream parsing mode. When this mode is enabled, then vmagent reads response from scrape target in chunks, then immediately processes every chunk and pushes the processed metrics to remote storage. This allows saving memory when scraping targets that expose millions of metrics.
Stream parsing mode is automatically enabled for scrape targets returning response bodies with sizes bigger than the -promscrape.minResponseSizeForStreamParse command-line flag value. Additionally, the stream parsing mode can be explicitly enabled in the following places:
- Via
-promscrape.streamParsecommand-line flag. In this case all the scrape targets defined in the file pointed by-promscrape.configare scraped in stream parsing mode. - Via
stream_parse: trueoption atscrape_configssection. In this case all the scrape targets defined in this section are scraped in stream parsing mode. - Via
__stream_parse__=truelabel, which can be set via relabeling atrelabel_configssection. In this case stream parsing mode is enabled for the corresponding scrape targets. Typical use case: to set the label via Kubernetes annotations for targets exposing big number of metrics.
Examples:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'big-federate'
stream_parse: true
static_configs:
- targets:
- big-prometeus1
- big-prometeus2
honor_labels: true
metrics_path: /federate
params:
'match[]': ['{__name__!=""}']
Note that sample_limit and series_limit options cannot be used in stream parsing mode because the parsed data is pushed to remote storage as soon as it is parsed.
Scraping big number of targets
A single vmagent instance can scrape tens of thousands of scrape targets. Sometimes this isn't enough due to limitations on CPU, network, RAM, etc.
In this case scrape targets can be split among multiple vmagent instances (aka vmagent horizontal scaling, sharding and clustering).
Each vmagent instance in the cluster must use identical -promscrape.config files with distinct -promscrape.cluster.memberNum values.
The flag value must be in the range 0 ... N-1, where N is the number of vmagent instances in the cluster.
The number of vmagent instances in the cluster must be passed to -promscrape.cluster.membersCount command-line flag. For example, the following commands
spread scrape targets among a cluster of two vmagent instances:
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.cluster.membersCount=2 -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=0 -promscrape.config=/path/to/config.yml ...
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.cluster.membersCount=2 -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=1 -promscrape.config=/path/to/config.yml ...
The -promscrape.cluster.memberNum can be set to a StatefulSet pod name when vmagent runs in Kubernetes. The pod name must end with a number in the range 0 ... promscrape.cluster.memberNum-1. For example, -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=vmagent-0.
By default each scrape target is scraped only by a single vmagent instance in the cluster. If there is a need for replicating scrape targets among multiple vmagent instances,
then -promscrape.cluster.replicationFactor command-line flag must be set to the desired number of replicas. For example, the following commands
start a cluster of three vmagent instances, where each target is scraped by two vmagent instances:
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.cluster.membersCount=3 -promscrape.cluster.replicationFactor=2 -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=0 -promscrape.config=/path/to/config.yml ...
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.cluster.membersCount=3 -promscrape.cluster.replicationFactor=2 -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=1 -promscrape.config=/path/to/config.yml ...
/path/to/vmagent -promscrape.cluster.membersCount=3 -promscrape.cluster.replicationFactor=2 -promscrape.cluster.memberNum=2 -promscrape.config=/path/to/config.yml ...
If each target is scraped by multiple vmagent instances, then data deduplication must be enabled at remote storage pointed by -remoteWrite.url.
The -dedup.minScrapeInterval must be set to the scrape_interval configured at -promscrape.config.
See these docs for details.
High availability
It is possible to run multiple identically configured vmagent instances or vmagent clusters,
so they scrape the same set of targets and push the collected data to the same set of VictoriaMetrics remote storage systems.
In this case the deduplication must be configured at VictoriaMetrics in order to de-duplicate samples received from multiple identically configured vmagent instances or clusters.
See these docs for details.
It is also recommended passing different values to -promscrape.cluster.name command-line flag per each vmagent instance or per each vmagent cluster in HA setup.
This is needed for proper data de-duplication. See this issue for details.
Scraping targets via a proxy
vmagent supports scraping targets via http, https and socks5 proxies. Proxy address must be specified in proxy_url option. For example, the following scrape config instructs
target scraping via https proxy at https://proxy-addr:1234:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: foo
proxy_url: https://proxy-addr:1234
Proxy can be configured with the following optional settings:
proxy_authorizationfor generic token authorization. See these docs.proxy_basic_authfor Basic authorization. See these docs.proxy_bearer_tokenandproxy_bearer_token_filefor Bearer token authorizationproxy_oauth2for OAuth2 config. See these docs.proxy_tls_configfor TLS config. See these docs.proxy_headersfor passing additional HTTP headers in requests to proxy.
For example:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: foo
proxy_url: https://proxy-addr:1234
proxy_basic_auth:
username: foobar
password: secret
proxy_tls_config:
insecure_skip_verify: true
cert_file: /path/to/cert
key_file: /path/to/key
ca_file: /path/to/ca
server_name: real-server-name
proxy_headers:
- "Proxy-Auth: top-secret"
Cardinality limiter
By default vmagent doesn't limit the number of time series each scrape target can expose. The limit can be enforced in the following places:
- Via
-promscrape.seriesLimitPerTargetcommand-line option. This limit is applied individually to all the scrape targets defined in the file pointed by-promscrape.config. - Via
series_limitconfig option atscrape_configsection. This limit is applied individually to all the scrape targets defined in the givenscrape_config. - Via
__series_limit__label, which can be set with relabeling atrelabel_configssection. This limit is applied to the corresponding scrape targets. Typical use case: to set the limit via Kubernetes annotations for targets, which may expose too high number of time series.
All the scraped metrics are dropped for time series exceeding the given limit. The exceeded limit can be monitored via promscrape_series_limit_rows_dropped_total metric.
See also sample_limit option at scrape_config section.
By default vmagent doesn't limit the number of time series written to remote storage systems specified at -remoteWrite.url. The limit can be enforced by setting the following command-line flags:
-remoteWrite.maxHourlySeries- limits the number of unique time seriesvmagentcan write to remote storage systems during the last hour. Useful for limiting the number of active time series.-remoteWrite.maxDailySeries- limits the number of unique time seriesvmagentcan write to remote storage systems during the last day. Useful for limiting daily churn rate.
Both limits can be set simultaneously. If any of these limits is reached, then samples for new time series are dropped instead of sending them to remote storage systems. A sample of dropped series is put in the log with WARNING level.
The exceeded limits can be monitored with the following metrics:
vmagent_hourly_series_limit_rows_dropped_total- the number of metrics dropped due to exceeded hourly limit on the number of unique time series.vmagent_daily_series_limit_rows_dropped_total- the number of metrics dropped due to exceeded daily limit on the number of unique time series.
These limits are approximate, so vmagent can underflow/overflow the limit by a small percentage (usually less than 1%).
Monitoring
vmagent exports various metrics in Prometheus exposition format at http://vmagent-host:8429/metrics page. We recommend setting up regular scraping of this page
either through vmagent itself or by Prometheus so that the exported metrics may be analyzed later.
Use official Grafana dashboard for vmagent state overview. Graphs on this dashboard contain useful hints - hover the i icon at the top left corner of each graph in order to read it.
If you have suggestions for improvements or have found a bug - please open an issue on github or add a review to the dashboard.
vmagent also exports the status for various targets at the following handlers:
-
http://vmagent-host:8429/targets. This handler returns human-readable status for every active target. This page is easy to query from the command line withwget,curlor similar tools. It accepts optionalshow_original_labels=1query arg which shows the original labels per each target before applying the relabeling. This information may be useful for debugging target relabeling. -
http://vmagent-host:8429/api/v1/targets. This handler returns data compatible with the corresponding page from Prometheus API. -
http://vmagent-host:8429/ready. This handler returns http 200 status code whenvmagentfinishes it's initialization for all service_discovery configs. It may be useful to performvmagentrolling update without any scrape loss.
Troubleshooting
-
We recommend you set up the official Grafana dashboard in order to monitor the state of `vmagent'.
-
We recommend you increase the maximum number of open files in the system (
ulimit -n) when scraping a big number of targets, asvmagentestablishes at least a single TCP connection per target. -
If
vmagentuses too big amounts of memory, then the following options can help:- Disabling staleness tracking with
-promscrape.noStaleMarkersoption. See these docs. - Enabling stream parsing mode if
vmagentscrapes targets with millions of metrics per target. See these docs. - Reducing the number of output queues with
-remoteWrite.queuescommand-line option. - Reducing the amounts of RAM vmagent can use for in-memory buffering with
-memory.allowedPercentor-memory.allowedBytescommand-line option. Another option is to reduce memory limits in Docker and/or Kubernetes ifvmagentruns under these systems. - Reducing the number of CPU cores vmagent can use by passing
GOMAXPROCS=Nenvironment variable tovmagent, whereNis the desired limit on CPU cores. Another option is to reduce CPU limits in Docker or Kubernetes ifvmagentruns under these systems. - Passing
-promscrape.dropOriginalLabelscommand-line option tovmagent, so it drops"discoveredLabels"and"droppedTargets"lists at/api/v1/targetspage. This reduces memory usage when scraping big number of targets at the cost of reduced debuggability for improperly configured per-target relabeling.
- Disabling staleness tracking with
-
When
vmagentscrapes many unreliable targets, it can flood the error log with scrape errors. These errors can be suppressed by passing-promscrape.suppressScrapeErrorscommand-line flag tovmagent. The most recent scrape error per each target can be observed athttp://vmagent-host:8429/targetsandhttp://vmagent-host:8429/api/v1/targets. -
The
/api/v1/targetspage could be useful for debugging relabeling process for scrape targets. This page contains original labels for targets dropped during relabeling (see "droppedTargets" section in the page output). By default the-promscrape.maxDroppedTargetstargets are shown here. If your setup drops more targets during relabeling, then increase-promscrape.maxDroppedTargetscommand-line flag value to see all the dropped targets. Note that tracking each dropped target requires up to 10Kb of RAM. Therefore big values for-promscrape.maxDroppedTargetsmay result in increased memory usage if a big number of scrape targets are dropped during relabeling. -
We recommend you increase
-remoteWrite.queuesifvmagent_remotewrite_pending_data_bytesmetric exported athttp://vmagent-host:8429/metricspage grows constantly. It is also recommended increasing-remoteWrite.maxBlockSizeand-remoteWrite.maxRowsPerBlockcommand-line options in this case. This can improve data ingestion performance to the configured remote storage systems at the cost of higher memory usage. -
If you see gaps in the data pushed by
vmagentto remote storage when-remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURLis set, try increasing-remoteWrite.queues. Such gaps may appear becausevmagentcannot keep up with sending the collected data to remote storage. Therefore it starts dropping the buffered data if the on-disk buffer size exceeds-remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURL. -
vmagentdrops data blocks if remote storage replies with400 Bad Requestand409 ConflictHTTP responses. The number of dropped blocks can be monitored viavmagent_remotewrite_packets_dropped_totalmetric exported at /metrics page. -
Use
-remoteWrite.queues=1when-remoteWrite.urlpoints to remote storage, which doesn't accept out-of-order samples (aka data backfilling). Such storage systems include Prometheus, Cortex and Thanos, which typically emitout of order sampleerrors. The best solution is to use remote storage with backfilling support. -
vmagentbuffers scraped data at the-remoteWrite.tmpDataPathdirectory until it is sent to-remoteWrite.url. The directory can grow large when remote storage is unavailable for extended periods of time and if-remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURLisn't set. If you don't want to send all the data from the directory to remote storage then simply stopvmagentand delete the directory. -
By default
vmagentmasks-remoteWrite.urlwithsecret-urlvalues in logs and at/metricspage because the url may contain sensitive information such as auth tokens or passwords. Pass-remoteWrite.showURLcommand-line flag when startingvmagentin order to see all the valid urls. -
By default
vmagentevenly spreads scrape load in time. If a particular scrape target must be scraped at the beginning of some interval, thenscrape_align_intervaloption must be used. For example, the following config aligns hourly scrapes to the beginning of hour:scrape_configs: - job_name: foo scrape_interval: 1h scrape_align_interval: 1h -
By default
vmagentevenly spreads scrape load in time. If a particular scrape target must be scraped at specific offset, thenscrape_offsetoption must be used. For example, the following config instructsvmagentto scrape the target at 10 seconds of every minute:scrape_configs: - job_name: foo scrape_interval: 1m scrape_offset: 10s -
If you see
skipping duplicate scrape target with identical labelserrors when scraping Kubernetes pods, then it is likely these pods listen to multiple ports or they use an init container. These errors can either be fixed or suppressed with the-promscrape.suppressDuplicateScrapeTargetErrorscommand-line flag. See the available options below if you prefer fixing the root cause of the error:The following relabeling rule may be added to
relabel_configssection in order to filter out pods with unneeded ports:- action: keep_if_equal source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port, __meta_kubernetes_pod_container_port_number]The following relabeling rule may be added to
relabel_configssection in order to filter out init container pods:- action: drop source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_init] regex: true
See also troubleshooting docs.
Kafka integration
Enterprise version of vmagent can read and write metrics from / to Kafka:
The enterprise version of vmagent is available for evaluation at releases page in vmutils-*-enteprise.tar.gz archives and in docker images with tags containing enterprise suffix.
Reading metrics from Kafka
Enterprise version of vmagent can read metrics in various formats from Kafka messages. These formats can be configured with -kafka.consumer.topic.defaultFormat or -kafka.consumer.topic.format command-line options. The following formats are supported:
promremotewrite- Prometheus remote_write. Messages in this format can be sent by vmagent - see these docs.influx- InfluxDB line protocol format.prometheus- Prometheus text exposition format and OpenMetrics format.graphite- Graphite plaintext format.jsonline- JSON line format.
Every Kafka message may contain multiple lines in influx, prometheus, graphite and jsonline format delimited by \n.
vmagent consumes messages from Kafka topics specified by -kafka.consumer.topic command-line flag. Multiple topics can be specified by passing multiple -kafka.consumer.topic command-line flags to vmagent.
vmagent consumes messages from Kafka brokers specified by -kafka.consumer.topic.brokers command-line flag. Multiple brokers can be specified per each -kafka.consumer.topic by passing a list of brokers delimited by ;. For example, -kafka.consumer.topic.brokers=host1:9092;host2:9092.
The following command starts vmagent, which reads metrics in InfluxDB line protocol format from Kafka broker at localhost:9092 from the topic metrics-by-telegraf and sends them to remote storage at http://localhost:8428/api/v1/write:
./bin/vmagent -remoteWrite.url=http://localhost:8428/api/v1/write \
-kafka.consumer.topic.brokers=localhost:9092 \
-kafka.consumer.topic.format=influx \
-kafka.consumer.topic=metrics-by-telegraf \
-kafka.consumer.topic.groupID=some-id
It is expected that Telegraf sends metrics to the metrics-by-telegraf topic with the following config:
[[outputs.kafka]]
brokers = ["localhost:9092"]
topic = "influx"
data_format = "influx"
Command-line flags for Kafka consumer
These command-line flags are available only in enterprise version of vmagent, which can be downloaded for evaluation from releases page (see vmutils-*-enteprise.tar.gz archives) and from docker images with tags containing enterprise suffix.
-kafka.consumer.topic array
Kafka topic names for data consumption.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.basicAuth.password array
Optional basic auth password for -kafka.consumer.topic. Must be used in conjunction with any supported auth methods for kafka client, specified by flag -kafka.consumer.topic.options='security.protocol=SASL_SSL;sasl.mechanisms=PLAIN'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.basicAuth.username array
Optional basic auth username for -kafka.consumer.topic. Must be used in conjunction with any supported auth methods for kafka client, specified by flag -kafka.consumer.topic.options='security.protocol=SASL_SSL;sasl.mechanisms=PLAIN'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.brokers array
List of brokers to connect for given topic, e.g. -kafka.consumer.topic.broker=host-1:9092;host-2:9092
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.defaultFormat string
Expected data format in the topic if -kafka.consumer.topic.format is skipped. (default "promremotewrite")
-kafka.consumer.topic.format array
data format for corresponding kafka topic. Valid formats: influx, prometheus, promremotewrite, graphite, jsonline
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.groupID array
Defines group.id for topic
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.isGzipped array
Enables gzip setting for topic messages payload. Only prometheus, jsonline and influx formats accept gzipped messages.
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.options array
Optional key=value;key1=value2 settings for topic consumer. See full configuration options at https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka/blob/master/CONFIGURATION.md.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
Writing metrics to Kafka
Enterprise version of vmagent writes data to Kafka with at-least-once semantics if -remoteWrite.url contains e.g. Kafka url. For example, if vmagent is started with -remoteWrite.url=kafka://localhost:9092/?topic=prom-rw, then it would send Prometheus remote_write messages to Kafka bootstrap server at localhost:9092 with the topic prom-rw. These messages can be read later from Kafka by another vmagent - see these docs for details.
Additional Kafka options can be passed as query params to -remoteWrite.url. For instance, kafka://localhost:9092/?topic=prom-rw&client.id=my-favorite-id sets client.id Kafka option to my-favorite-id. The full list of Kafka options is available here.
Kafka broker authorization and authentication
Two types of auth are supported:
- sasl with username and password:
./bin/vmagent -remoteWrite.url=kafka://localhost:9092/?topic=prom-rw&security.protocol=SASL_SSL&sasl.mechanisms=PLAIN -remoteWrite.basicAuth.username=user -remoteWrite.basicAuth.password=password
- tls certificates:
./bin/vmagent -remoteWrite.url=kafka://localhost:9092/?topic=prom-rw&security.protocol=SSL -remoteWrite.tlsCAFile=/opt/ca.pem -remoteWrite.tlsCertFile=/opt/cert.pem -remoteWrite.tlsKeyFile=/opt/key.pem
How to build from sources
We recommend using binary releases - vmagent is located in the vmutils-* archives .
Development build
- Install Go. The minimum supported version is Go 1.18.
- Run
make vmagentfrom the root folder of the repository. It builds thevmagentbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
Production build
- Install docker.
- Run
make vmagent-prodfrom the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmagent-prodbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
Building docker images
Run make package-vmagent. It builds victoriametrics/vmagent:<PKG_TAG> docker image locally.
<PKG_TAG> is an auto-generated image tag, which depends on source code in the repository.
The <PKG_TAG> may be manually set via PKG_TAG=foobar make package-vmagent.
The base docker image is alpine but it is possible to use any other base image
by setting it via <ROOT_IMAGE> environment variable. For example, the following command builds the image on top of scratch image:
ROOT_IMAGE=scratch make package-vmagent
ARM build
ARM build may run on Raspberry Pi or on energy-efficient ARM servers.
Development ARM build
- Install Go. The minimum supported version is Go 1.18.
- Run
make vmagent-linux-armormake vmagent-linux-arm64from the root folder of the repository It buildsvmagent-linux-armorvmagent-linux-arm64binary respectively and puts it into thebinfolder.
Production ARM build
- Install docker.
- Run
make vmagent-linux-arm-prodormake vmagent-linux-arm64-prodfrom the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmagent-linux-arm-prodorvmagent-linux-arm64-prodbinary respectively and puts it into thebinfolder.
Profiling
vmagent provides handlers for collecting the following Go profiles:
- Memory profile can be collected with the following command (replace
0.0.0.0with hostname if needed):
curl http://0.0.0.0:8429/debug/pprof/heap > mem.pprof
- CPU profile can be collected with the following command (replace
0.0.0.0with hostname if needed):
curl http://0.0.0.0:8429/debug/pprof/profile > cpu.pprof
The command for collecting CPU profile waits for 30 seconds before returning.
The collected profiles may be analyzed with go tool pprof.
Advanced usage
vmagent can be fine-tuned with various command-line flags. Run ./vmagent -help in order to see the full list of these flags with their desciptions and default values:
./vmagent -help
vmagent collects metrics data via popular data ingestion protocols and routes them to VictoriaMetrics.
See the docs at https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html .
-configAuthKey string
Authorization key for accessing /config page. It must be passed via authKey query arg
-csvTrimTimestamp duration
Trim timestamps when importing csv data to this duration. Minimum practical duration is 1ms. Higher duration (i.e. 1s) may be used for reducing disk space usage for timestamp data (default 1ms)
-datadog.maxInsertRequestSize size
The maximum size in bytes of a single DataDog POST request to /api/v1/series
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 67108864)
-denyQueryTracing
Whether to disable the ability to trace queries. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#query-tracing
-dryRun
Whether to check only config files without running vmagent. The following files are checked: -promscrape.config, -remoteWrite.relabelConfig, -remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig . Unknown config entries aren't allowed in -promscrape.config by default. This can be changed by passing -promscrape.config.strictParse=false command-line flag
-enableTCP6
Whether to enable IPv6 for listening and dialing. By default only IPv4 TCP and UDP is used
-envflag.enable
Whether to enable reading flags from environment variables additionally to command line. Command line flag values have priority over values from environment vars. Flags are read only from command line if this flag isn't set. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#environment-variables for more details
-envflag.prefix string
Prefix for environment variables if -envflag.enable is set
-eula
By specifying this flag, you confirm that you have an enterprise license and accept the EULA https://victoriametrics.com/assets/VM_EULA.pdf
-flagsAuthKey string
Auth key for /flags endpoint. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides httpAuth.* settings
-fs.disableMmap
Whether to use pread() instead of mmap() for reading data files. By default mmap() is used for 64-bit arches and pread() is used for 32-bit arches, since they cannot read data files bigger than 2^32 bytes in memory. mmap() is usually faster for reading small data chunks than pread()
-graphiteListenAddr string
TCP and UDP address to listen for Graphite plaintext data. Usually :2003 must be set. Doesn't work if empty
-graphiteTrimTimestamp duration
Trim timestamps for Graphite data to this duration. Minimum practical duration is 1s. Higher duration (i.e. 1m) may be used for reducing disk space usage for timestamp data (default 1s)
-http.connTimeout duration
Incoming http connections are closed after the configured timeout. This may help to spread the incoming load among a cluster of services behind a load balancer. Please note that the real timeout may be bigger by up to 10% as a protection against the thundering herd problem (default 2m0s)
-http.disableResponseCompression
Disable compression of HTTP responses to save CPU resources. By default compression is enabled to save network bandwidth
-http.idleConnTimeout duration
Timeout for incoming idle http connections (default 1m0s)
-http.maxGracefulShutdownDuration duration
The maximum duration for a graceful shutdown of the HTTP server. A highly loaded server may require increased value for a graceful shutdown (default 7s)
-http.pathPrefix string
An optional prefix to add to all the paths handled by http server. For example, if '-http.pathPrefix=/foo/bar' is set, then all the http requests will be handled on '/foo/bar/*' paths. This may be useful for proxied requests. See https://www.robustperception.io/using-external-urls-and-proxies-with-prometheus
-http.shutdownDelay duration
Optional delay before http server shutdown. During this delay, the server returns non-OK responses from /health page, so load balancers can route new requests to other servers
-httpAuth.password string
Password for HTTP Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if -httpAuth.username is empty
-httpAuth.username string
Username for HTTP Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if empty. See also -httpAuth.password
-httpListenAddr string
TCP address to listen for http connections. Set this flag to empty value in order to disable listening on any port. This mode may be useful for running multiple vmagent instances on the same server. Note that /targets and /metrics pages aren't available if -httpListenAddr='' (default ":8429")
-import.maxLineLen size
The maximum length in bytes of a single line accepted by /api/v1/import; the line length can be limited with 'max_rows_per_line' query arg passed to /api/v1/export
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 104857600)
-influx.databaseNames array
Comma-separated list of database names to return from /query and /influx/query API. This can be needed for accepting data from Telegraf plugins such as https://github.com/fangli/fluent-plugin-influxdb
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-influx.maxLineSize size
The maximum size in bytes for a single InfluxDB line during parsing
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 262144)
-influxDBLabel string
Default label for the DB name sent over '?db={db_name}' query parameter (default "db")
-influxListenAddr string
TCP and UDP address to listen for InfluxDB line protocol data. Usually :8089 must be set. Doesn't work if empty. This flag isn't needed when ingesting data over HTTP - just send it to http://<vmagent>:8429/write
-influxMeasurementFieldSeparator string
Separator for '{measurement}{separator}{field_name}' metric name when inserted via InfluxDB line protocol (default "_")
-influxSkipMeasurement
Uses '{field_name}' as a metric name while ignoring '{measurement}' and '-influxMeasurementFieldSeparator'
-influxSkipSingleField
Uses '{measurement}' instead of '{measurement}{separator}{field_name}' for metic name if InfluxDB line contains only a single field
-influxTrimTimestamp duration
Trim timestamps for InfluxDB line protocol data to this duration. Minimum practical duration is 1ms. Higher duration (i.e. 1s) may be used for reducing disk space usage for timestamp data (default 1ms)
-insert.maxQueueDuration duration
The maximum duration for waiting in the queue for insert requests due to -maxConcurrentInserts (default 1m0s)
-kafka.consumer.topic array
Kafka topic names for data consumption.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.basicAuth.password array
Optional basic auth password for -kafka.consumer.topic. Must be used in conjunction with any supported auth methods for kafka client, specified by flag -kafka.consumer.topic.options='security.protocol=SASL_SSL;sasl.mechanisms=PLAIN'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.basicAuth.username array
Optional basic auth username for -kafka.consumer.topic. Must be used in conjunction with any supported auth methods for kafka client, specified by flag -kafka.consumer.topic.options='security.protocol=SASL_SSL;sasl.mechanisms=PLAIN'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.brokers array
List of brokers to connect for given topic, e.g. -kafka.consumer.topic.broker=host-1:9092;host-2:9092
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.defaultFormat string
Expected data format in the topic if -kafka.consumer.topic.format is skipped. (default "promremotewrite")
-kafka.consumer.topic.format array
data format for corresponding kafka topic. Valid formats: influx, prometheus, promremotewrite, graphite, jsonline
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.groupID array
Defines group.id for topic
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.isGzipped array
Enables gzip setting for topic messages payload. Only prometheus, jsonline and influx formats accept gzipped messages.
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-kafka.consumer.topic.options array
Optional key=value;key1=value2 settings for topic consumer. See full configuration options at https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka/blob/master/CONFIGURATION.md.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-loggerDisableTimestamps
Whether to disable writing timestamps in logs
-loggerErrorsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of ERROR messages. If more than the given number of errors are emitted per second, the remaining errors are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-loggerFormat string
Format for logs. Possible values: default, json (default "default")
-loggerLevel string
Minimum level of errors to log. Possible values: INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, PANIC (default "INFO")
-loggerOutput string
Output for the logs. Supported values: stderr, stdout (default "stderr")
-loggerTimezone string
Timezone to use for timestamps in logs. Timezone must be a valid IANA Time Zone. For example: America/New_York, Europe/Berlin, Etc/GMT+3 or Local (default "UTC")
-loggerWarnsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of WARN messages. If more than the given number of warns are emitted per second, then the remaining warns are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-maxConcurrentInserts int
The maximum number of concurrent inserts. Default value should work for most cases, since it minimizes the overhead for concurrent inserts. This option is tigthly coupled with -insert.maxQueueDuration (default 16)
-maxInsertRequestSize size
The maximum size in bytes of a single Prometheus remote_write API request
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 33554432)
-memory.allowedBytes size
Allowed size of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. This option overrides -memory.allowedPercent if set to a non-zero value. Too low a value may increase the cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from OS page cache resulting in higher disk IO usage
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 0)
-memory.allowedPercent float
Allowed percent of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. See also -memory.allowedBytes. Too low a value may increase cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from OS page cache which will result in higher disk IO usage (default 60)
-metricsAuthKey string
Auth key for /metrics endpoint. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides httpAuth.* settings
-opentsdbHTTPListenAddr string
TCP address to listen for OpentTSDB HTTP put requests. Usually :4242 must be set. Doesn't work if empty
-opentsdbListenAddr string
TCP and UDP address to listen for OpentTSDB metrics. Telnet put messages and HTTP /api/put messages are simultaneously served on TCP port. Usually :4242 must be set. Doesn't work if empty
-opentsdbTrimTimestamp duration
Trim timestamps for OpenTSDB 'telnet put' data to this duration. Minimum practical duration is 1s. Higher duration (i.e. 1m) may be used for reducing disk space usage for timestamp data (default 1s)
-opentsdbhttp.maxInsertRequestSize size
The maximum size of OpenTSDB HTTP put request
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 33554432)
-opentsdbhttpTrimTimestamp duration
Trim timestamps for OpenTSDB HTTP data to this duration. Minimum practical duration is 1ms. Higher duration (i.e. 1s) may be used for reducing disk space usage for timestamp data (default 1ms)
-pprofAuthKey string
Auth key for /debug/pprof/* endpoints. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides httpAuth.* settings
-promscrape.azureSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in Azure. This works only if azure_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#azure_sd_config for details (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.cluster.memberNum string
The number of number in the cluster of scrapers. It must be an unique value in the range 0 ... promscrape.cluster.membersCount-1 across scrapers in the cluster. Can be specified as pod name of Kubernetes StatefulSet - pod-name-Num, where Num is a numeric part of pod name (default "0")
-promscrape.cluster.membersCount int
The number of members in a cluster of scrapers. Each member must have an unique -promscrape.cluster.memberNum in the range 0 ... promscrape.cluster.membersCount-1 . Each member then scrapes roughly 1/N of all the targets. By default cluster scraping is disabled, i.e. a single scraper scrapes all the targets
-promscrape.cluster.name string
Optional name of the cluster. If multiple vmagent clusters scrape the same targets, then each cluster must have unique name in order to properly de-duplicate samples received from these clusters. See https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/VictoriaMetrics/issues/2679
-promscrape.cluster.replicationFactor int
The number of members in the cluster, which scrape the same targets. If the replication factor is greater than 1, then the deduplication must be enabled at remote storage side. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#deduplication (default 1)
-promscrape.config string
Optional path to Prometheus config file with 'scrape_configs' section containing targets to scrape. The path can point to local file and to http url. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#how-to-scrape-prometheus-exporters-such-as-node-exporter for details
-promscrape.config.dryRun
Checks -promscrape.config file for errors and unsupported fields and then exits. Returns non-zero exit code on parsing errors and emits these errors to stderr. See also -promscrape.config.strictParse command-line flag. Pass -loggerLevel=ERROR if you don't need to see info messages in the output.
-promscrape.config.strictParse
Whether to deny unsupported fields in -promscrape.config . Set to false in order to silently skip unsupported fields (default true)
-promscrape.configCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in '-promscrape.config' file. By default the checking is disabled. Send SIGHUP signal in order to force config check for changes
-promscrape.consul.waitTime duration
Wait time used by Consul service discovery. Default value is used if not set
-promscrape.consulSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in Consul. This works only if consul_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#consul_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.digitaloceanSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in digital ocean. This works only if digitalocean_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#digitalocean_sd_config for details (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.disableCompression
Whether to disable sending 'Accept-Encoding: gzip' request headers to all the scrape targets. This may reduce CPU usage on scrape targets at the cost of higher network bandwidth utilization. It is possible to set 'disable_compression: true' individually per each 'scrape_config' section in '-promscrape.config' for fine grained control
-promscrape.disableKeepAlive
Whether to disable HTTP keep-alive connections when scraping all the targets. This may be useful when targets has no support for HTTP keep-alive connection. It is possible to set 'disable_keepalive: true' individually per each 'scrape_config' section in '-promscrape.config' for fine grained control. Note that disabling HTTP keep-alive may increase load on both vmagent and scrape targets
-promscrape.discovery.concurrency int
The maximum number of concurrent requests to Prometheus autodiscovery API (Consul, Kubernetes, etc.) (default 100)
-promscrape.discovery.concurrentWaitTime duration
The maximum duration for waiting to perform API requests if more than -promscrape.discovery.concurrency requests are simultaneously performed (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.dnsSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in dns. This works only if dns_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#dns_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.dockerSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in docker. This works only if docker_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#docker_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.dockerswarmSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in dockerswarm. This works only if dockerswarm_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#dockerswarm_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.dropOriginalLabels
Whether to drop original labels for scrape targets at /targets and /api/v1/targets pages. This may be needed for reducing memory usage when original labels for big number of scrape targets occupy big amounts of memory. Note that this reduces debuggability for improper per-target relabeling configs
-promscrape.ec2SDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in ec2. This works only if ec2_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#ec2_sd_config for details (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.eurekaSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in eureka. This works only if eureka_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#eureka_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.fileSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in 'file_sd_config'. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#file_sd_config for details (default 5m0s)
-promscrape.gceSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in gce. This works only if gce_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#gce_sd_config for details (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.httpSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in http endpoint service discovery. This works only if http_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#http_sd_config for details (default 1m0s)
-promscrape.kubernetes.apiServerTimeout duration
How frequently to reload the full state from Kubernetes API server (default 30m0s)
-promscrape.kubernetesSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in Kubernetes API server. This works only if kubernetes_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#kubernetes_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.maxDroppedTargets int
The maximum number of droppedTargets to show at /api/v1/targets page. Increase this value if your setup drops more scrape targets during relabeling and you need investigating labels for all the dropped targets. Note that the increased number of tracked dropped targets may result in increased memory usage (default 1000)
-promscrape.maxResponseHeadersSize size
The maximum size of http response headers from Prometheus scrape targets
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 4096)
-promscrape.maxScrapeSize size
The maximum size of scrape response in bytes to process from Prometheus targets. Bigger responses are rejected
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 16777216)
-promscrape.minResponseSizeForStreamParse size
The minimum target response size for automatic switching to stream parsing mode, which can reduce memory usage. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#stream-parsing-mode
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 1000000)
-promscrape.noStaleMarkers
Whether to disable sending Prometheus stale markers for metrics when scrape target disappears. This option may reduce memory usage if stale markers aren't needed for your setup. This option also disables populating the scrape_series_added metric. See https://prometheus.io/docs/concepts/jobs_instances/#automatically-generated-labels-and-time-series
-promscrape.openstackSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in openstack API server. This works only if openstack_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. See https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/configuration/configuration/#openstack_sd_config for details (default 30s)
-promscrape.seriesLimitPerTarget int
Optional limit on the number of unique time series a single scrape target can expose. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#cardinality-limiter for more info
-promscrape.streamParse
Whether to enable stream parsing for metrics obtained from scrape targets. This may be useful for reducing memory usage when millions of metrics are exposed per each scrape target. It is posible to set 'stream_parse: true' individually per each 'scrape_config' section in '-promscrape.config' for fine grained control
-promscrape.suppressDuplicateScrapeTargetErrors
Whether to suppress 'duplicate scrape target' errors; see https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#troubleshooting for details
-promscrape.suppressScrapeErrors
Whether to suppress scrape errors logging. The last error for each target is always available at '/targets' page even if scrape errors logging is suppressed. See also -promscrape.suppressScrapeErrorsDelay
-promscrape.suppressScrapeErrorsDelay duration
The delay for suppressing repeated scrape errors logging per each scrape targets. This may be used for reducing the number of log lines related to scrape errors. See also -promscrape.suppressScrapeErrors
-promscrape.yandexcloudSDCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in Yandex Cloud API. This works only if yandexcloud_sd_configs is configured in '-promscrape.config' file. (default 30s)
-pushmetrics.extraLabel array
Optional labels to add to metrics pushed to -pushmetrics.url . For example, -pushmetrics.extraLabel='instance="foo"' adds instance="foo" label to all the metrics pushed to -pushmetrics.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-pushmetrics.interval duration
Interval for pushing metrics to -pushmetrics.url (default 10s)
-pushmetrics.url array
Optional URL to push metrics exposed at /metrics page. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#push-metrics . By default metrics exposed at /metrics page aren't pushed to any remote storage
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.accessKey array
Optional AWS AccessKey to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.ec2Endpoint array
Optional AWS EC2 API endpoint to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.region array
Optional AWS region to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.roleARN array
Optional AWS roleARN to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.secretKey array
Optional AWS SecretKey to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.service array
Optional AWS Service to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set. Defaults to "aps"
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.stsEndpoint array
Optional AWS STS API endpoint to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url if -remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 is set
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.aws.useSigv4 array
Enables SigV4 request signing for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. It is expected that other -remoteWrite.aws.* command-line flags are set if sigv4 request signing is enabled
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.password array
Optional basic auth password to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.passwordFile array
Optional path to basic auth password to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. The file is re-read every second
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.username array
Optional basic auth username to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.bearerToken array
Optional bearer auth token to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.bearerTokenFile array
Optional path to bearer token file to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. The token is re-read from the file every second
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.flushInterval duration
Interval for flushing the data to remote storage. This option takes effect only when less than 10K data points per second are pushed to -remoteWrite.url (default 1s)
-remoteWrite.headers array
Optional HTTP headers to send with each request to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. For example, -remoteWrite.headers='My-Auth:foobar' would send 'My-Auth: foobar' HTTP header with every request to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. Multiple headers must be delimited by '^^': -remoteWrite.headers='header1:value1^^header2:value2'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.label array
Optional label in the form 'name=value' to add to all the metrics before sending them to -remoteWrite.url. Pass multiple -remoteWrite.label flags in order to add multiple labels to metrics before sending them to remote storage
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.maxBlockSize size
The maximum block size to send to remote storage. Bigger blocks may improve performance at the cost of the increased memory usage. See also -remoteWrite.maxRowsPerBlock
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 8388608)
-remoteWrite.maxDailySeries int
The maximum number of unique series vmagent can send to remote storage systems during the last 24 hours. Excess series are logged and dropped. This can be useful for limiting series churn rate. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#cardinality-limiter
-remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURL size
The maximum file-based buffer size in bytes at -remoteWrite.tmpDataPath for each -remoteWrite.url. When buffer size reaches the configured maximum, then old data is dropped when adding new data to the buffer. Buffered data is stored in ~500MB chunks, so the minimum practical value for this flag is 500MB. Disk usage is unlimited if the value is set to 0
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 0)
-remoteWrite.maxHourlySeries int
The maximum number of unique series vmagent can send to remote storage systems during the last hour. Excess series are logged and dropped. This can be useful for limiting series cardinality. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#cardinality-limiter
-remoteWrite.maxRowsPerBlock int
The maximum number of samples to send in each block to remote storage. Higher number may improve performance at the cost of the increased memory usage. See also -remoteWrite.maxBlockSize (default 10000)
-remoteWrite.multitenantURL array
Base path for multitenant remote storage URL to write data to. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#multitenancy for details. Example url: http://<vminsert>:8480 . Pass multiple -remoteWrite.multitenantURL flags in order to replicate data to multiple remote storage systems. See also -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.oauth2.clientID array
Optional OAuth2 clientID to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.oauth2.clientSecret array
Optional OAuth2 clientSecret to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.oauth2.clientSecretFile array
Optional OAuth2 clientSecretFile to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.oauth2.scopes array
Optional OAuth2 scopes to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. Scopes must be delimited by ';'
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.oauth2.tokenUrl array
Optional OAuth2 tokenURL to use for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.proxyURL array
Optional proxy URL for writing data to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. Supported proxies: http, https, socks5. Example: -remoteWrite.proxyURL=socks5://proxy:1234
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.queues int
The number of concurrent queues to each -remoteWrite.url. Set more queues if default number of queues isn't enough for sending high volume of collected data to remote storage. Default value is 2 * numberOfAvailableCPUs (default 8)
-remoteWrite.rateLimit array
Optional rate limit in bytes per second for data sent to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. By default the rate limit is disabled. It can be useful for limiting load on remote storage when big amounts of buffered data is sent after temporary unavailability of the remote storage
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.relabelConfig string
Optional path to file with relabel_config entries. The path can point either to local file or to http url. These entries are applied to all the metrics before sending them to -remoteWrite.url. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/vmagent.html#relabeling for details
-remoteWrite.relabelDebug
Whether to log metrics before and after relabeling with -remoteWrite.relabelConfig. If the -remoteWrite.relabelDebug is enabled, then the metrics aren't sent to remote storage. This is useful for debugging the relabeling configs
-remoteWrite.roundDigits array
Round metric values to this number of decimal digits after the point before writing them to remote storage. Examples: -remoteWrite.roundDigits=2 would round 1.236 to 1.24, while -remoteWrite.roundDigits=-1 would round 126.78 to 130. By default digits rounding is disabled. Set it to 100 for disabling it for a particular remote storage. This option may be used for improving data compression for the stored metrics
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.sendTimeout array
Timeout for sending a single block of data to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.showURL
Whether to show -remoteWrite.url in the exported metrics. It is hidden by default, since it can contain sensitive info such as auth key
-remoteWrite.significantFigures array
The number of significant figures to leave in metric values before writing them to remote storage. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Significant_figures . Zero value saves all the significant figures. This option may be used for improving data compression for the stored metrics. See also -remoteWrite.roundDigits
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tlsCAFile array
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. By default system CA is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tlsCertFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tlsInsecureSkipVerify array
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tlsKeyFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tlsServerName array
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. By default the server name from -remoteWrite.url is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.tmpDataPath string
Path to directory where temporary data for remote write component is stored. See also -remoteWrite.maxDiskUsagePerURL (default "vmagent-remotewrite-data")
-remoteWrite.url array
Remote storage URL to write data to. It must support Prometheus remote_write API. It is recommended using VictoriaMetrics as remote storage. Example url: http://<victoriametrics-host>:8428/api/v1/write . Pass multiple -remoteWrite.url flags in order to replicate data to multiple remote storage systems. See also -remoteWrite.multitenantURL
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig array
Optional path to relabel config for the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. The path can point either to local file or to http url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-remoteWrite.urlRelabelDebug array
Whether to log metrics before and after relabeling with -remoteWrite.urlRelabelConfig. If the -remoteWrite.urlRelabelDebug is enabled, then the metrics aren't sent to the corresponding -remoteWrite.url. This is useful for debugging the relabeling configs
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-sortLabels
Whether to sort labels for incoming samples before writing them to all the configured remote storage systems. This may be needed for reducing memory usage at remote storage when the order of labels in incoming samples is random. For example, if m{k1="v1",k2="v2"} may be sent as m{k2="v2",k1="v1"}Enabled sorting for labels can slow down ingestion performance a bit
-tls
Whether to enable TLS for incoming HTTP requests at -httpListenAddr (aka https). -tlsCertFile and -tlsKeyFile must be set if -tls is set
-tlsCertFile string
Path to file with TLS certificate if -tls is set. Prefer ECDSA certs instead of RSA certs as RSA certs are slower. The provided certificate file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated
-tlsCipherSuites array
Optional list of TLS cipher suites for incoming requests over HTTPS if -tls is set. See the list of supported cipher suites at https://pkg.go.dev/crypto/tls#pkg-constants
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-tlsKeyFile string
Path to file with TLS key if -tls is set. The provided key file is automatically re-read every second, so it can be dynamically updated
-version
Show VictoriaMetrics version