The bump was required for `vmalert` package. `vmalert` docs now also contain an updated description. Signed-off-by: hagen1778 <roman@victoriametrics.com>
42 KiB
vmalert
vmalert executes a list of the given alerting
or recording
rules against configured -datasource.url. For sending alerting notifications
vmalert relies on Alertmanager configured via -notifier.url flag.
Recording rules results are persisted via remote write
protocol and require -remoteWrite.url to be configured.
Vmalert is heavily inspired by Prometheus
implementation and aims to be compatible with its syntax.
Features
- Integration with VictoriaMetrics TSDB;
- VictoriaMetrics MetricsQL support and expressions validation;
- Prometheus alerting rules definition format support;
- Integration with Alertmanager;
- Keeps the alerts state on restarts;
- Graphite datasource can be used for alerting and recording rules. See these docs;
- Recording and Alerting rules backfilling (aka
replay). See these docs; - Lightweight without extra dependencies.
Limitations
vmalertexecute queries against remote datasource which has reliability risks because of the network. It is recommended to configure alerts thresholds and rules expressions with the understanding that network requests may fail;- by default, rules execution is sequential within one group, but persistence of execution results to remote storage is asynchronous. Hence, user shouldn't rely on chaining of recording rules when result of previous recording rule is reused in the next one;
QuickStart
To build vmalert from sources:
git clone https://github.com/VictoriaMetrics/VictoriaMetrics
cd VictoriaMetrics
make vmalert
The build binary will be placed in VictoriaMetrics/bin folder.
To start using vmalert you will need the following things:
- list of rules - PromQL/MetricsQL expressions to execute;
- datasource address - reachable MetricsQL endpoint to run queries against;
- notifier address [optional] - reachable Alert Manager instance for processing, aggregating alerts, and sending notifications.
- remote write address [optional] - remote write compatible storage to persist rules and alerts state info;
- remote read address [optional] - MetricsQL compatible datasource to restore alerts state from.
Then configure vmalert accordingly:
./bin/vmalert -rule=alert.rules \ # Path to the file with rules configuration. Supports wildcard
-datasource.url=http://localhost:8428 \ # PromQL compatible datasource
-notifier.url=http://localhost:9093 \ # AlertManager URL (required if alerting rules are used)
-notifier.url=http://127.0.0.1:9093 \ # AlertManager replica URL
-remoteWrite.url=http://localhost:8428 \ # Remote write compatible storage to persist rules and alerts state info (required if recording rules are used)
-remoteRead.url=http://localhost:8428 \ # MetricsQL compatible datasource to restore alerts state from
-external.label=cluster=east-1 \ # External label to be applied for each rule
-external.label=replica=a # Multiple external labels may be set
Note there's a separate remoteRead.url to allow writing results of
alerting/recording rules into a different storage than the initial data that's
queried. This allows using vmalert to aggregate data from a short-term,
high-frequency, high-cardinality storage into a long-term storage with
decreased cardinality and a bigger interval between samples.
See the full list of configuration flags in configuration section.
If you run multiple vmalert services for the same datastore or AlertManager - do not forget
to specify different external.label flags in order to define which vmalert generated rules or alerts.
Configuration for recording
and alerting rules is very
similar to Prometheus rules and configured using YAML. Configuration examples may be found
in testdata folder.
Every rule belongs to a group and every configuration file may contain arbitrary number of groups:
groups:
[ - <rule_group> ]
Groups
Each group has the following attributes:
# The name of the group. Must be unique within a file.
name: <string>
# How often rules in the group are evaluated.
[ interval: <duration> | default = -evaluationInterval flag ]
# How many rules execute at once within a group. Increasing concurrency may speed
# up round execution speed.
[ concurrency: <integer> | default = 1 ]
# Optional type for expressions inside the rules. Supported values: "graphite" and "prometheus".
# By default "prometheus" type is used.
[ type: <string> ]
# Optional list of label filters applied to every rule's
# request withing a group. Is compatible only with VM datasource.
# See more details at https://docs.victoriametrics.com#prometheus-querying-api-enhancements
extra_filter_labels:
[ <labelname>: <labelvalue> ... ]
# Optional list of labels added to every rule within a group.
# It has priority over the external labels.
# Labels are commonly used for adding environment
# or tenant-specific tag.
labels:
[ <labelname>: <labelvalue> ... ]
rules:
[ - <rule> ... ]
Rules
Every rule contains expr field for PromQL
or MetricsQL expression. Vmalert will execute the configured
expression and then act according to the Rule type.
There are two types of Rules:
- alerting -
Alerting rules allow defining alert conditions via
exprfield and to send notifications to Alertmanager if execution result is not empty. - recording -
Recording rules allow defining
exprwhich result will be then backfilled to configured-remoteWrite.url. Recording rules are used to precompute frequently needed or computationally expensive expressions and save their result as a new set of time series.
vmalert forbids defining duplicates - rules with the same combination of name, expression, and labels
within one group.
Alerting rules
The syntax for alerting rule is the following:
# The name of the alert. Must be a valid metric name.
alert: <string>
# The expression to evaluate. The expression language depends on the type value.
# By default PromQL/MetricsQL expression is used. If group.type="graphite", then the expression
# must contain valid Graphite expression.
expr: <string>
# Alerts are considered firing once they have been returned for this long.
# Alerts which have not yet been fired for long enough are considered pending.
# If param is omitted or set to 0 then alerts will be immediately considered
# as firing once they return.
[ for: <duration> | default = 0s ]
# Labels to add or overwrite for each alert.
labels:
[ <labelname>: <tmpl_string> ]
# Annotations to add to each alert.
annotations:
[ <labelname>: <tmpl_string> ]
It is allowed to use Go templating in annotations
to format data, iterate over it or execute expressions.
Additionally, vmalert provides some extra templating functions
listed here.
Recording rules
The syntax for recording rules is following:
# The name of the time series to output to. Must be a valid metric name.
record: <string>
# The expression to evaluate. The expression language depends on the type value.
# By default MetricsQL expression is used. If group.type="graphite", then the expression
# must contain valid Graphite expression.
expr: <string>
# Labels to add or overwrite before storing the result.
labels:
[ <labelname>: <labelvalue> ]
For recording rules to work -remoteWrite.url must be specified.
Alerts state on restarts
vmalert has no local storage, so alerts state is stored in the process memory. Hence, after restart of vmalert
the process alerts state will be lost. To avoid this situation, vmalert should be configured via the following flags:
-remoteWrite.url- URL to VictoriaMetrics (Single) or vminsert (Cluster).vmalertwill persist alerts state into the configured address in the form of time series namedALERTSandALERTS_FOR_STATEvia remote-write protocol. These are regular time series and maybe queried from VM just as any other time series. The state is stored to the configured address on every rule evaluation.-remoteRead.url- URL to VictoriaMetrics (Single) or vmselect (Cluster).vmalertwill try to restore alerts state from configured address by querying time series with nameALERTS_FOR_STATE.
Both flags are required for proper state restoration. Restore process may fail if time series are missing
in configured -remoteRead.url, weren't updated in the last 1h (controlled by -remoteRead.lookback)
or received state doesn't match current vmalert rules configuration.
Multitenancy
There are the following approaches exist for alerting and recording rules across multiple tenants:
-
To run a separate
vmalertinstance per each tenant. The corresponding tenant must be specified in-datasource.urlcommand-line flag according to these docs. For example,/path/to/vmalert -datasource.url=http://vmselect:8481/select/123/prometheuswould run alerts againstAccountID=123. For recording rules the-remoteWrite.urlcommand-line flag must contain the url for the specific tenant as well. For example,-remoteWrite.url=http://vminsert:8480/insert/123/prometheuswould write recording rules toAccountID=123. -
To specify
tenantparameter per each alerting and recording group if enterprise version of vmalert is used with-clusterModecommand-line flag. For example:
groups:
- name: rules_for_tenant_123
tenant: "123"
rules:
# Rules for accountID=123
- name: rules_for_tenant_456:789
tenant: "456:789"
rules:
# Rules for accountID=456, projectID=789
If -clusterMode is enabled, then -datasource.url, -remoteRead.url and -remoteWrite.url must
contain only the hostname without tenant id. For example: -datasource.url=http://vmselect:8481.
vmalert automatically adds the specified tenant to urls per each recording rule in this case.
If -clusterMode is enabled and the tenant in a particular group is missing, then the tenant value
is obtained from -defaultTenant.prometheus or -defaultTenant.graphite depending on the type of the group.
The enterprise version of vmalert is available in vmutils-*-enterprise.tar.gz files
at release page and in *-enterprise
tags at Docker Hub.
Topology examples
The following sections are showing how vmalert may be used and configured
for different scenarios.
Please note, not all flags in examples are required:
-remoteWrite.urland-remoteRead.urlare optional and are needed only if you have recording rules or want to store alerts state onvmalertrestarts;-notifier.urlis optional and is needed only if you have alerting rules.
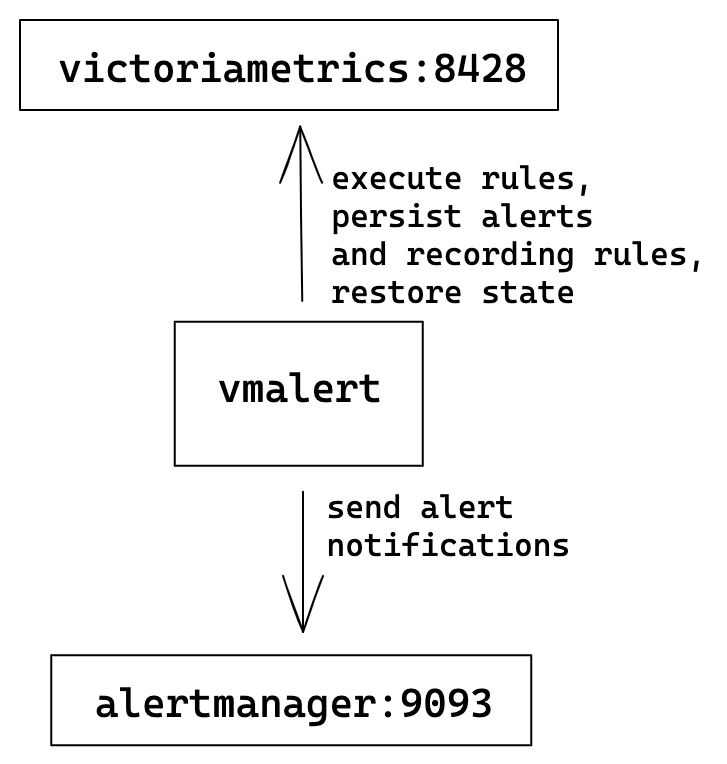
Single-node VictoriaMetrics
The simplest configuration where one single-node VM server is used for rules execution, storing recording rules results and alerts state.
vmalert configuration flags:
./bin/vmalert -rule=rules.yml \ # Path to the file with rules configuration. Supports wildcard
-datasource.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr for executing rules expressions
-remoteWrite.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr to persist alerts state and recording rules results
-remoteRead.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr for restoring alerts state after restart
-notifier.url=http://alertmanager:9093 # AlertManager addr to send alerts when they trigger
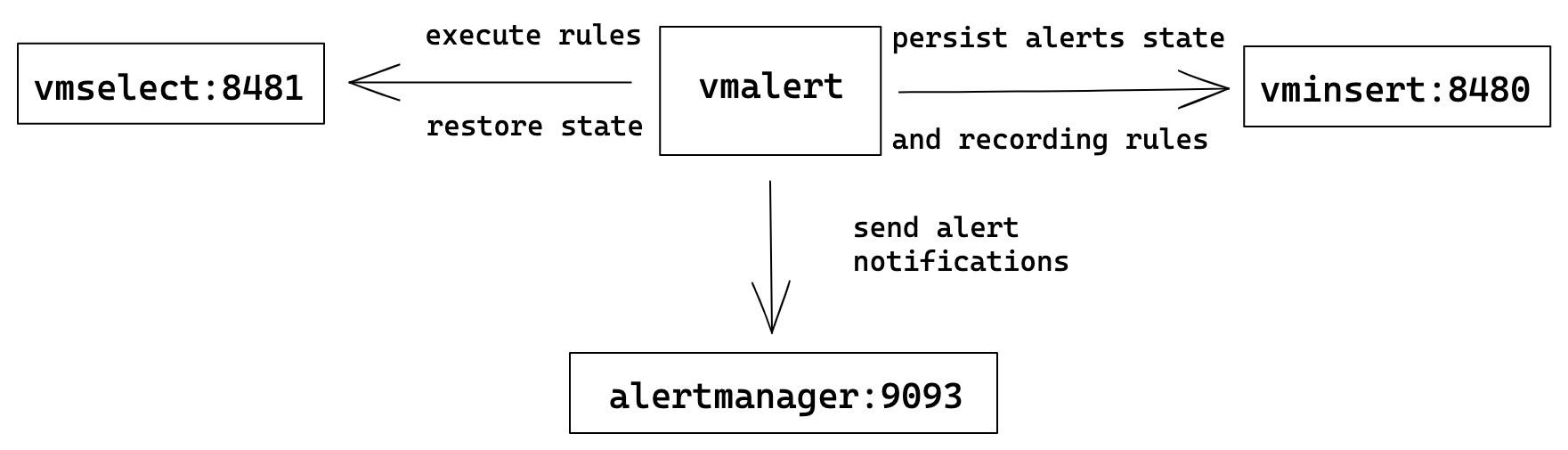
Cluster VictoriaMetrics
In cluster mode
VictoriaMetrics has separate components for writing and reading path:
vminsert and vmselect components respectively. vmselect is used for executing rules expressions
and vminsert is used to persist recording rules results and alerts state.
Cluster mode could have multiple vminsert and vmselect components.
vmalert configuration flags:
./bin/vmalert -rule=rules.yml \ # Path to the file with rules configuration. Supports wildcard
-datasource.url=http://vmselect:8481/select/0/prometheus # vmselect addr for executing rules expressions
-remoteWrite.url=http://vminsert:8480/insert/0/prometheuss # vminsert addr to persist alerts state and recording rules results
-remoteRead.url=http://vmselect:8481/select/0/prometheus # vmselect addr for restoring alerts state after restart
-notifier.url=http://alertmanager:9093 # AlertManager addr to send alerts when they trigger
In case when you want to spread the load on these components - add balancers before them and configure
vmalert with balancer's addresses. Please, see more about VM's cluster architecture
here.
HA vmalert
For HA user can run multiple identically configured vmalert instances.
It means all of them will execute the same rules, write state and results to
the same destinations, and send alert notifications to multiple configured
Alertmanagers.
vmalert configuration flags:
./bin/vmalert -rule=rules.yml \ # Path to the file with rules configuration. Supports wildcard
-datasource.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr for executing rules expressions
-remoteWrite.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr to persist alerts state and recording rules results
-remoteRead.url=http://victoriametrics:8428 \ # VM-single addr for restoring alerts state after restart
-notifier.url=http://alertmanager1:9093 \ # Multiple AlertManager addresses to send alerts when they trigger
-notifier.url=http://alertmanagerN:9093 # The same alert will be sent to all configured notifiers
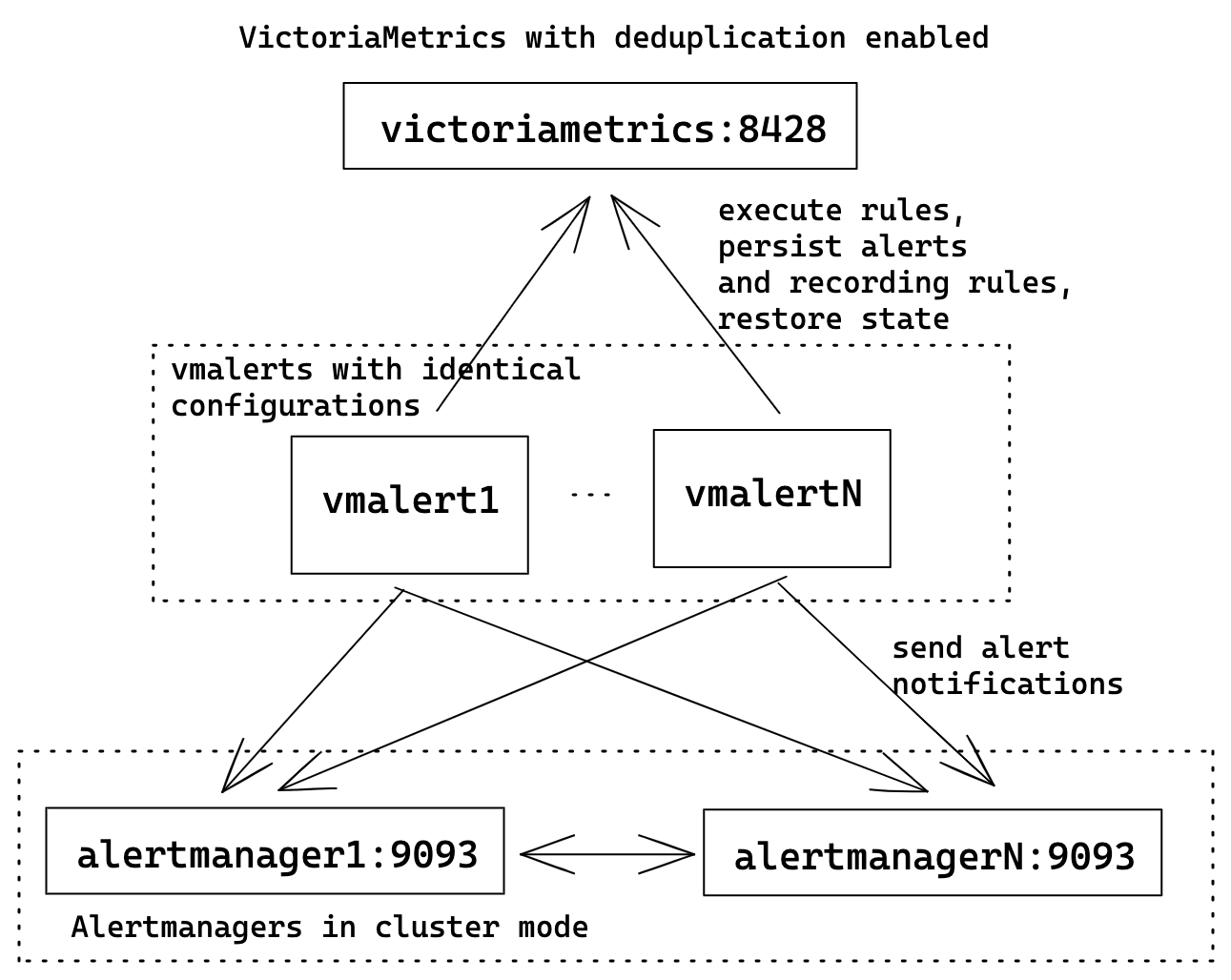
To avoid recording rules results and alerts state duplication in VictoriaMetrics server don't forget to configure deduplication.
Alertmanager will automatically deduplicate alerts with identical labels, so ensure that
all vmalerts are having the same config.
Don't forget to configure cluster mode for Alertmanagers for better reliability.
This example uses single-node VM server for the sake of simplicity. Check how to replace it with cluster VictoriaMetrics if needed.
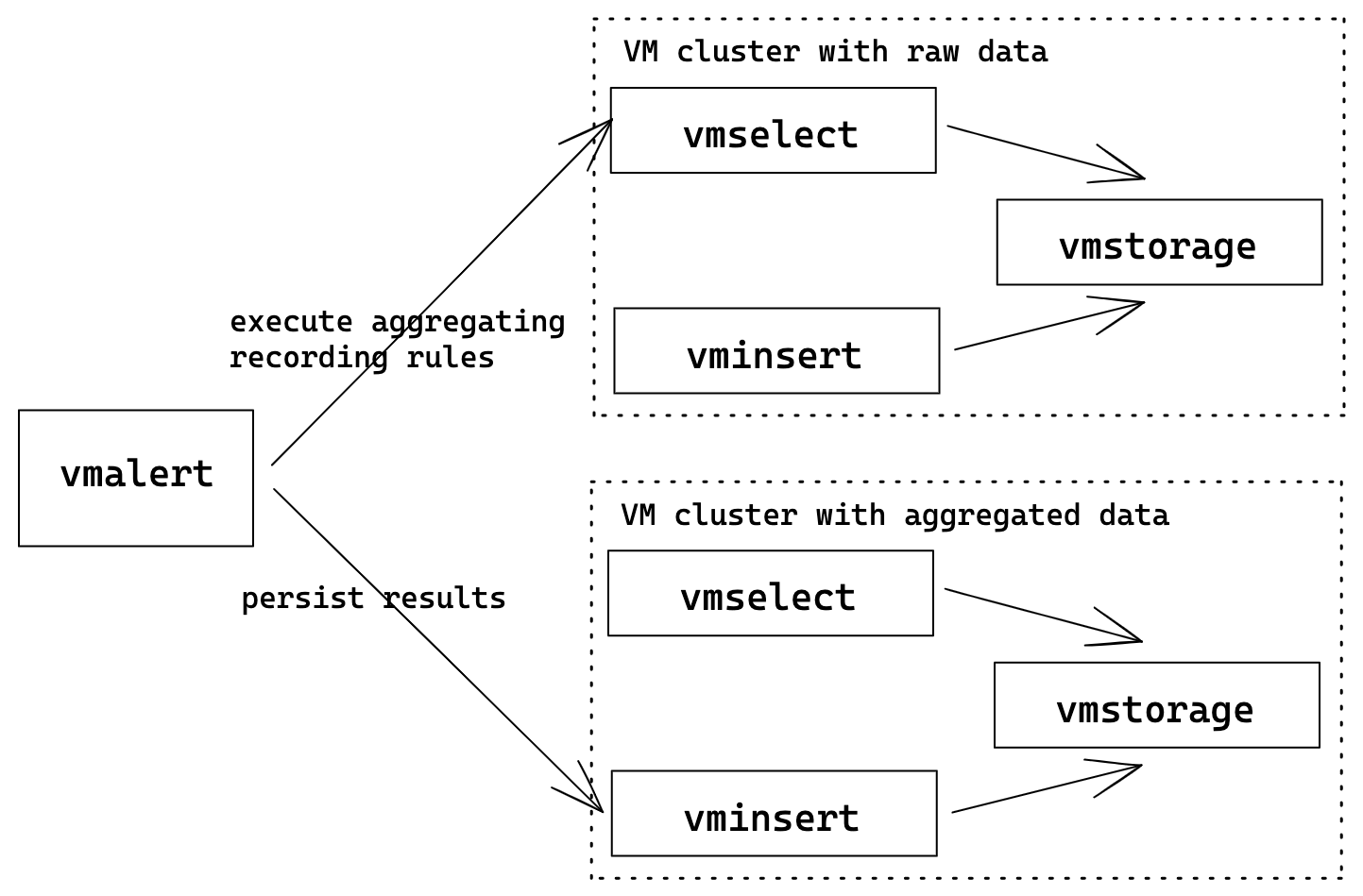
Downsampling and aggregation via vmalert
Example shows how to build a topology where vmalert will process data from one cluster
and write results into another. Such clusters may be called as "hot" (low retention,
high-speed disks, used for operative monitoring) and "cold" (long term retention,
slower/cheaper disks, low resolution data). With help of vmalert, user can setup
recording rules to process raw data from "hot" cluster (by applying additional transformations
or reducing resolution) and push results to "cold" cluster.
vmalert configuration flags:
./bin/vmalert -rule=downsampling-rules.yml \ # Path to the file with rules configuration. Supports wildcard
-datasource.url=http://raw-cluster-vmselect:8481/select/0/prometheus # vmselect addr for executing recordi ng rules expressions
-remoteWrite.url=http://aggregated-cluster-vminsert:8480/insert/0/prometheuss # vminsert addr to persist recording rules results
Please note, replay feature may be used for transforming historical data.
Flags -remoteRead.url and -notifier.url are omitted since we assume only recording rules are used.
Web
vmalert runs a web-server (-httpListenAddr) for serving metrics and alerts endpoints:
http://<vmalert-addr>- UI;http://<vmalert-addr>/api/v1/groups- list of all loaded groups and rules;http://<vmalert-addr>/api/v1/alerts- list of all active alerts;http://<vmalert-addr>/api/v1/<groupID>/<alertID>/status"- get alert status by ID. Used as alert source in AlertManager.http://<vmalert-addr>/metrics- application metrics.http://<vmalert-addr>/-/reload- hot configuration reload.
Graphite
vmalert sends requests to <-datasource.url>/render?format=json during evaluation of alerting and recording rules
if the corresponding group or rule contains type: "graphite" config option. It is expected that the <-datasource.url>/render
implements Graphite Render API for format=json.
When using vmalert with both graphite and prometheus rules configured against cluster version of VM do not forget
to set -datasource.appendTypePrefix flag to true, so vmalert can adjust URL prefix automatically based on the query type.
Rules backfilling
vmalert supports alerting and recording rules backfilling (aka replay). In replay mode vmalert
can read the same rules configuration as normal, evaluate them on the given time range and backfill
results via remote write to the configured storage. vmalert supports any PromQL/MetricsQL compatible
data source for backfilling.
How it works
In replay mode vmalert works as a cli-tool and exits immediately after work is done.
To run vmalert in replay mode:
./bin/vmalert -rule=path/to/your.rules \ # path to files with rules you usually use with vmalert
-datasource.url=http://localhost:8428 \ # PromQL/MetricsQL compatible datasource
-remoteWrite.url=http://localhost:8428 \ # remote write compatible storage to persist results
-replay.timeFrom=2021-05-11T07:21:43Z \ # time from begin replay
-replay.timeTo=2021-05-29T18:40:43Z # time to finish replay
The output of the command will look like the following:
Replay mode:
from: 2021-05-11 07:21:43 +0000 UTC # set by -replay.timeFrom
to: 2021-05-29 18:40:43 +0000 UTC # set by -replay.timeTo
max data points per request: 1000 # set by -replay.maxDatapointsPerQuery
Group "ReplayGroup"
interval: 1m0s
requests to make: 27
max range per request: 16h40m0s
> Rule "type:vm_cache_entries:rate5m" (ID: 1792509946081842725)
27 / 27 [----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------] 100.00% 78 p/s
> Rule "go_cgo_calls_count:rate5m" (ID: 17958425467471411582)
27 / 27 [-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------] 100.00% ? p/s
Group "vmsingleReplay"
interval: 30s
requests to make: 54
max range per request: 8h20m0s
> Rule "RequestErrorsToAPI" (ID: 17645863024999990222)
54 / 54 [-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------] 100.00% ? p/s
> Rule "TooManyLogs" (ID: 9042195394653477652)
54 / 54 [-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------] 100.00% ? p/s
2021-06-07T09:59:12.098Z info app/vmalert/replay.go:68 replay finished! Imported 511734 samples
In replay mode all groups are executed sequentially one-by-one. Rules within the group are
executed sequentially as well (concurrency setting is ignored). Vmalert sends rule's expression
to /query_range endpoint
of the configured -datasource.url. Returned data is then processed according to the rule type and
backfilled to -remoteWrite.url via remote Write protocol.
Vmalert respects evaluationInterval value set by flag or per-group during the replay.
Vmalert automatically disables caching on VictoriaMetrics side by sending nocache=1 param. It allows
to prevent cache pollution and unwanted time range boundaries adjustment during backfilling.
Recording rules
The result of recording rules replay should match with results of normal rules evaluation.
Alerting rules
The result of alerting rules replay is time series reflecting alert's state.
To see if replayed alert has fired in the past use the following PromQL/MetricsQL expression:
ALERTS{alertname="your_alertname", alertstate="firing"}
Execute the query against storage which was used for -remoteWrite.url during the replay.
Additional configuration
There are following non-required replay flags:
-replay.maxDatapointsPerQuery- the max number of data points expected to receive in one request. In two words, it affects the max time range for every/query_rangerequest. The higher the value, the fewer requests will be issued duringreplay.-replay.ruleRetryAttempts- when datasource fails to respond vmalert will make this number of retries per rule before giving up.-replay.rulesDelay- delay between sequential rules execution. Important in cases if there are chaining (rules which depend on each other) rules. It is expected, that remote storage will be able to persist previously accepted data during the delay, so data will be available for the subsequent queries. Keep it equal or bigger than-remoteWrite.flushInterval.
See full description for these flags in ./vmalert --help.
Limitations
- Graphite engine isn't supported yet;
querytemplate function is disabled for performance reasons (might be changed in future);
Monitoring
vmalert exports various metrics in Prometheus exposition format at http://vmalert-host:8880/metrics page.
We recommend setting up regular scraping of this page either through vmagent or by Prometheus so that the exported
metrics may be analyzed later.
Use the official Grafana dashboard for vmalert overview. Graphs on this dashboard contain useful hints - hover the i icon at the top left corner of each graph in order to read it.
If you have suggestions for improvements or have found a bug - please open an issue on github or add
a review to the dashboard.
Configuration
Pass -help to vmalert in order to see the full list of supported
command-line flags with their descriptions.
The shortlist of configuration flags is the following:
-datasource.appendTypePrefix
Whether to add type prefix to -datasource.url based on the query type. Set to true if sending different query types to the vmselect URL.
-datasource.basicAuth.password string
Optional basic auth password for -datasource.url
-datasource.basicAuth.passwordFile string
Optional path to basic auth password to use for -datasource.url
-datasource.basicAuth.username string
Optional basic auth username for -datasource.url
-datasource.bearerToken string
Optional bearer auth token to use for -datasource.url.
-datasource.bearerTokenFile string
Optional path to bearer token file to use for -datasource.url.
-datasource.lookback duration
Lookback defines how far into the past to look when evaluating queries. For example, if the datasource.lookback=5m then param "time" with value now()-5m will be added to every query.
-datasource.maxIdleConnections int
Defines the number of idle (keep-alive connections) to each configured datasource. Consider setting this value equal to the value: groups_total * group.concurrency. Too low a value may result in a high number of sockets in TIME_WAIT state. (default 100)
-datasource.queryStep duration
queryStep defines how far a value can fallback to when evaluating queries. For example, if datasource.queryStep=15s then param "step" with value "15s" will be added to every query.If queryStep isn't specified, rule's evaluationInterval will be used instead.
-datasource.roundDigits int
Adds "round_digits" GET param to datasource requests. In VM "round_digits" limits the number of digits after the decimal point in response values.
-datasource.tlsCAFile string
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to -datasource.url. By default, system CA is used
-datasource.tlsCertFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to -datasource.url
-datasource.tlsInsecureSkipVerify
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to -datasource.url
-datasource.tlsKeyFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to -datasource.url
-datasource.tlsServerName string
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to -datasource.url. By default, the server name from -datasource.url is used
-datasource.url string
VictoriaMetrics or vmselect url. Required parameter. E.g. http://127.0.0.1:8428
-disableAlertgroupLabel
Whether to disable adding group's name as label to generated alerts and time series.
-dryRun -rule
Whether to check only config files without running vmalert. The rules file are validated. The -rule flag must be specified.
-enableTCP6
Whether to enable IPv6 for listening and dialing. By default only IPv4 TCP and UDP is used
-envflag.enable
Whether to enable reading flags from environment variables additionally to command line. Command line flag values have priority over values from environment vars. Flags are read only from command line if this flag isn't set. See https://docs.victoriametrics.com/#environment-variables for more details
-envflag.prefix string
Prefix for environment variables if -envflag.enable is set
-evaluationInterval duration
How often to evaluate the rules (default 1m0s)
-external.alert.source string
External Alert Source allows to override the Source link for alerts sent to AlertManager for cases where you want to build a custom link to Grafana, Prometheus or any other service.
eg. 'explore?orgId=1&left=[\"now-1h\",\"now\",\"VictoriaMetrics\",{\"expr\": \"{{$expr|quotesEscape|crlfEscape|queryEscape}}\"},{\"mode\":\"Metrics\"},{\"ui\":[true,true,true,\"none\"]}]'.If empty '/api/v1/:groupID/alertID/status' is used
-external.label array
Optional label in the form 'name=value' to add to all generated recording rules and alerts. Pass multiple -label flags in order to add multiple label sets.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-external.url string
External URL is used as alert's source for sent alerts to the notifier
-fs.disableMmap
Whether to use pread() instead of mmap() for reading data files. By default mmap() is used for 64-bit arches and pread() is used for 32-bit arches, since they cannot read data files bigger than 2^32 bytes in memory. mmap() is usually faster for reading small data chunks than pread()
-http.connTimeout duration
Incoming http connections are closed after the configured timeout. This may help to spread the incoming load among a cluster of services behind a load balancer. Please note that the real timeout may be bigger by up to 10% as a protection against the thundering herd problem (default 2m0s)
-http.disableResponseCompression
Disable compression of HTTP responses to save CPU resources. By default compression is enabled to save network bandwidth
-http.idleConnTimeout duration
Timeout for incoming idle http connections (default 1m0s)
-http.maxGracefulShutdownDuration duration
The maximum duration for a graceful shutdown of the HTTP server. A highly loaded server may require increased value for a graceful shutdown (default 7s)
-http.pathPrefix string
An optional prefix to add to all the paths handled by http server. For example, if '-http.pathPrefix=/foo/bar' is set, then all the http requests will be handled on '/foo/bar/*' paths. This may be useful for proxied requests. See https://www.robustperception.io/using-external-urls-and-proxies-with-prometheus
-http.shutdownDelay duration
Optional delay before http server shutdown. During this delay, the server returns non-OK responses from /health page, so load balancers can route new requests to other servers
-httpAuth.password string
Password for HTTP Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if -httpAuth.username is empty
-httpAuth.username string
Username for HTTP Basic Auth. The authentication is disabled if empty. See also -httpAuth.password
-httpListenAddr string
Address to listen for http connections (default ":8880")
-loggerDisableTimestamps
Whether to disable writing timestamps in logs
-loggerErrorsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of ERROR messages. If more than the given number of errors are emitted per second, the remaining errors are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-loggerFormat string
Format for logs. Possible values: default, json (default "default")
-loggerLevel string
Minimum level of errors to log. Possible values: INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, PANIC (default "INFO")
-loggerOutput string
Output for the logs. Supported values: stderr, stdout (default "stderr")
-loggerTimezone string
Timezone to use for timestamps in logs. Timezone must be a valid IANA Time Zone. For example: America/New_York, Europe/Berlin, Etc/GMT+3 or Local (default "UTC")
-loggerWarnsPerSecondLimit int
Per-second limit on the number of WARN messages. If more than the given number of warns are emitted per second, then the remaining warns are suppressed. Zero values disable the rate limit
-memory.allowedBytes size
Allowed size of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. This option overrides -memory.allowedPercent if set to a non-zero value. Too low a value may increase the cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from OS page cache resulting in higher disk IO usage
Supports the following optional suffixes for size values: KB, MB, GB, KiB, MiB, GiB (default 0)
-memory.allowedPercent float
Allowed percent of system memory VictoriaMetrics caches may occupy. See also -memory.allowedBytes. Too low a value may increase cache miss rate usually resulting in higher CPU and disk IO usage. Too high a value may evict too much data from OS page cache which will result in higher disk IO usage (default 60)
-metricsAuthKey string
Auth key for /metrics. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides httpAuth.* settings
-notifier.basicAuth.password array
Optional basic auth password for -notifier.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.basicAuth.username array
Optional basic auth username for -notifier.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.tlsCAFile array
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to -notifier.url. By default system CA is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.tlsCertFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to -notifier.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.tlsInsecureSkipVerify array
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to -notifier.url
Supports array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.tlsKeyFile array
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to -notifier.url
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.tlsServerName array
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to -notifier.url. By default the server name from -notifier.url is used
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-notifier.url array
Prometheus alertmanager URL, e.g. http://127.0.0.1:9093
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-pprofAuthKey string
Auth key for /debug/pprof. It must be passed via authKey query arg. It overrides httpAuth.* settings
-remoteRead.basicAuth.password string
Optional basic auth password for -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.basicAuth.passwordFile string
Optional path to basic auth password to use for -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.basicAuth.username string
Optional basic auth username for -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.bearerToken string
Optional bearer auth token to use for -remoteRead.url.
-remoteRead.bearerTokenFile string
Optional path to bearer token file to use for -remoteRead.url.
-remoteRead.disablePathAppend
Whether to disable automatic appending of '/api/v1/query' path to the configured -remoteRead.url.
-remoteRead.ignoreRestoreErrors
Whether to ignore errors from remote storage when restoring alerts state on startup. (default true)
-remoteRead.lookback duration
Lookback defines how far to look into past for alerts timeseries. For example, if lookback=1h then range from now() to now()-1h will be scanned. (default 1h0m0s)
-remoteRead.tlsCAFile string
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to -remoteRead.url. By default system CA is used
-remoteRead.tlsCertFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.tlsInsecureSkipVerify
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.tlsKeyFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to -remoteRead.url
-remoteRead.tlsServerName string
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to -remoteRead.url. By default the server name from -remoteRead.url is used
-remoteRead.url vmalert
Optional URL to VictoriaMetrics or vmselect that will be used to restore alerts state. This configuration makes sense only if vmalert was configured with `remoteWrite.url` before and has been successfully persisted its state. E.g. http://127.0.0.1:8428. See also -remoteRead.disablePathAppend
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.password string
Optional basic auth password for -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.passwordFile string
Optional path to basic auth password to use for -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.basicAuth.username string
Optional basic auth username for -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.bearerToken string
Optional bearer auth token to use for -remoteWrite.url.
-remoteWrite.bearerTokenFile string
Optional path to bearer token file to use for -remoteWrite.url.
-remoteWrite.concurrency int
Defines number of writers for concurrent writing into remote querier (default 1)
-remoteWrite.disablePathAppend
Whether to disable automatic appending of '/api/v1/write' path to the configured -remoteWrite.url.
-remoteWrite.flushInterval duration
Defines interval of flushes to remote write endpoint (default 5s)
-remoteWrite.maxBatchSize int
Defines defines max number of timeseries to be flushed at once (default 1000)
-remoteWrite.maxQueueSize int
Defines the max number of pending datapoints to remote write endpoint (default 100000)
-remoteWrite.tlsCAFile string
Optional path to TLS CA file to use for verifying connections to -remoteWrite.url. By default system CA is used
-remoteWrite.tlsCertFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate file to use when connecting to -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.tlsInsecureSkipVerify
Whether to skip tls verification when connecting to -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.tlsKeyFile string
Optional path to client-side TLS certificate key to use when connecting to -remoteWrite.url
-remoteWrite.tlsServerName string
Optional TLS server name to use for connections to -remoteWrite.url. By default the server name from -remoteWrite.url is used
-remoteWrite.url string
Optional URL to VictoriaMetrics or vminsert where to persist alerts state and recording rules results in form of timeseries. For example, if -remoteWrite.url=http://127.0.0.1:8428 is specified, then the alerts state will be written to http://127.0.0.1:8428/api/v1/write . See also -remoteWrite.disablePathAppend
-replay.maxDatapointsPerQuery int
Max number of data points expected in one request. The higher the value, the less requests will be made during replay. (default 1000)
-replay.ruleRetryAttempts int
Defines how many retries to make before giving up on rule if request for it returns an error. (default 5)
-replay.rulesDelay duration
Delay between rules evaluation within the group. Could be important if there are chained rules inside of the groupand processing need to wait for previous rule results to be persisted by remote storage before evaluating the next rule.Keep it equal or bigger than -remoteWrite.flushInterval. (default 1s)
-replay.timeFrom string
The time filter in RFC3339 format to select time series with timestamp equal or higher than provided value. E.g. '2020-01-01T20:07:00Z'
-replay.timeTo string
The time filter in RFC3339 format to select timeseries with timestamp equal or lower than provided value. E.g. '2020-01-01T20:07:00Z'
-rule array
Path to the file with alert rules.
Supports patterns. Flag can be specified multiple times.
Examples:
-rule="/path/to/file". Path to a single file with alerting rules
-rule="dir/*.yaml" -rule="/*.yaml". Relative path to all .yaml files in "dir" folder,
absolute path to all .yaml files in root.
Rule files may contain %{ENV_VAR} placeholders, which are substituted by the corresponding env vars.
Supports an array of values separated by comma or specified via multiple flags.
-rule.configCheckInterval duration
Interval for checking for changes in '-rule' files. By default the checking is disabled. Send SIGHUP signal in order to force config check for changes
-rule.maxResolveDuration duration
Limits the maximum duration for automatic alert expiration, which is by default equal to 3 evaluation intervals of the parent group.
-rule.validateExpressions
Whether to validate rules expressions via MetricsQL engine (default true)
-rule.validateTemplates
Whether to validate annotation and label templates (default true)
-tls
Whether to enable TLS (aka HTTPS) for incoming requests. -tlsCertFile and -tlsKeyFile must be set if -tls is set
-tlsCertFile string
Path to file with TLS certificate. Used only if -tls is set. Prefer ECDSA certs instead of RSA certs as RSA certs are slower
-tlsKeyFile string
Path to file with TLS key. Used only if -tls is set
-version
Show VictoriaMetrics version
vmalert supports "hot" config reload via the following methods:
- send SIGHUP signal to
vmalertprocess; - send GET request to
/-/reloadendpoint; - configure
-rule.configCheckIntervalflag for periodic reload on config change.
Contributing
vmalert is mostly designed and built by VictoriaMetrics community.
Feel free to share your experience and ideas for improving this
software. Please keep simplicity as the main priority.
How to build from sources
It is recommended using binary releases
vmalertis located invmutils-*archives there.
Development build
- Install Go. The minimum supported version is Go 1.17.
- Run
make vmalertfrom the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmalertbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
Production build
- Install docker.
- Run
make vmalert-prodfrom the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmalert-prodbinary and puts it into thebinfolder.
ARM build
ARM build may run on Raspberry Pi or on energy-efficient ARM servers.
Development ARM build
- Install Go. The minimum supported version is Go 1.17.
- Run
make vmalert-armormake vmalert-arm64from the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmalert-armorvmalert-arm64binary respectively and puts it into thebinfolder.
Production ARM build
- Install docker.
- Run
make vmalert-arm-prodormake vmalert-arm64-prodfrom the root folder of the repository. It buildsvmalert-arm-prodorvmalert-arm64-prodbinary respectively and puts it into thebinfolder.